Fig. 3.
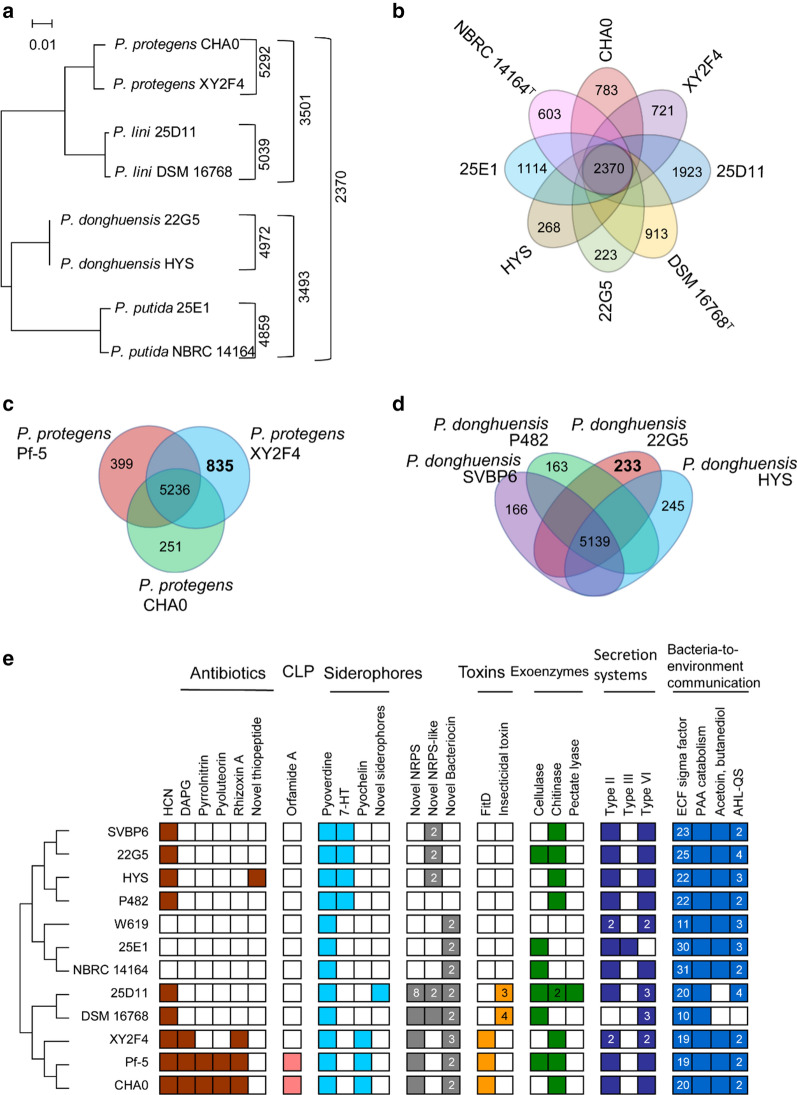
Comparative genome analysis of Pseudomonas strains. a, b Number of shared genes and unique genes in genomes and of P. protegens XY2F4, P. donghuensis 22G5, P. putida 25E1 and P. lini 25D11 and their type strains. c, d Number of unique genes in P. protegens XY2F4XY2F4 and P. donghuensis 22G5 when compared with published strains from the same species (with NCBI accessions). e Presence of selected gene clusters for biosynthesis of antibiotics, cyclic lipopeptides (CLP), siderophores, insecticidal toxins, exoenzymes, secretion systems, and chemicals for bacteria-to-environment communication. Colored box/blank box indicates the presence/absence of selected gene clusters, respectively. Numbers within boxes represent the predicted number of gene clusters encoded for the corresponding products