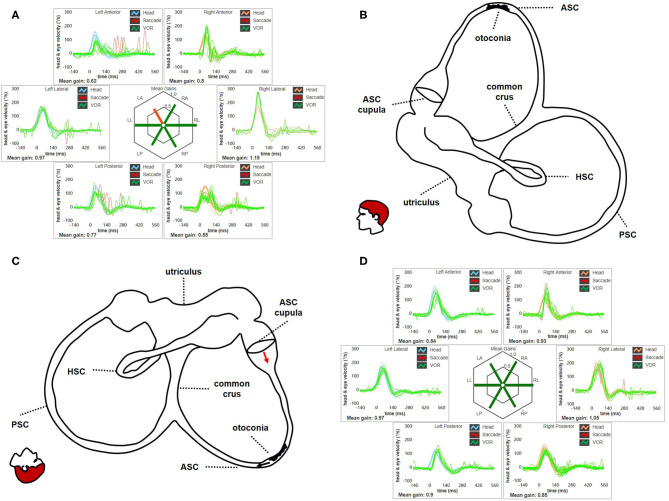
Figure 13.
(A) Presenting vHIT of subject # 45 affected by BPPV involving the ampullary arm of left ASC. Mean value of VOR-gain (eye velocity/head velocity) is reported for each canal. The hexagonal plot in the center of the figure summarizes mean VOR-gains for each canal; normal gains are shown in green and deficient gains are in red. Selective slight deficient VOR-gain for left ASC (0.62) with scattered overt saccades can be observed. (B) Representation for left membranous labyrinth and patient's head along the sagittal (pitch) plane in upright position to explain the site settled by otoconia at presentation. Debris are located within a nearly horizontal tract of the canal, where possible narrowing or irregularities could allow them to settle without resulting in nystagmus in upright position. In this condition, otoliths are thought to partly occlude the canal lumen resulting in an incomplete canalith jam acting as “low-pass filter” for ampullary receptor, thus preventing high-frequency stimuli as detect by vHIT. (C) Representation of the disposition of otoconia after SHH test. In this position, otoconia may slowly shift toward the non-ampullary tract of the canal below (black arrow) due to gravity. Resulting excitatory endolymphatic movement should lead ASC cupula to bend ampullofugally (red arrow), accounting for pDBN in recumbent positions. (D) vHIT findings after performing CRP for ASC-BPPV leading to return of particles within the utriculus and resolution of symptoms and signs. VOR-gain value for left ASC is back within normal range (0.84). ASC, anterior semicircular canal; BPPV, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; CRP, canalith repositioning procedure; HSC, horizontal semicircular canal; LA, left anterior; LL, left lateral; LP, left posterior. pDBN, positional downbeat nystagmus; PSC, posterior semicircular canal; RA, right anterior; RL, right lateral; RP, right posterior; SHH, straight head hanging; vHIT, video-head impulse test; VOR, vestibulo-ocular reflex.