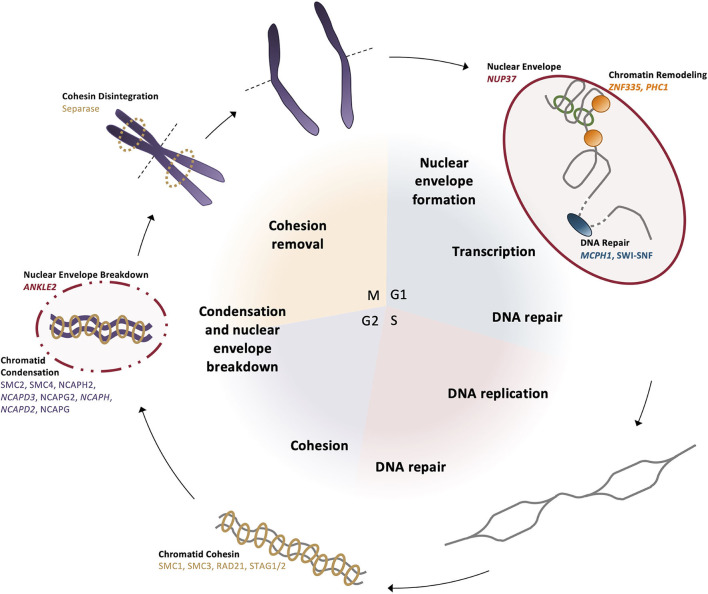
Figure 5.
DNA dynamics are linked to the cell cycle. (G1 phase) The nuclear envelope reforms after mitosis, then chromatin is positioned in the nucleus and remodeled for transcription by ZNF335 and PHC1. In preparation for synthesis and the G1 cell cycle checkpoint, DNA repair proteins correct any damage present in the genome. (S phase) Chromosomes undergo replication and repair proteins correct any errors or DNA breaks that occurred during the synthesis process. (G2 phase) Sister chromatids are brought together and bound by cohesin complexes. Prior to mitotic entry, condensin II begins the condensation of the chromatids as the negative regulator MCPH1 is broken down. (M phase) Nuclear envelope is broken down by ANKLE2 and homologous chromosomes align at the metaphase plate. Separase disintegrates the cohesin bonds between sister chromatids so they can be segregated to opposite poles before cytokinesis divides the daughter cells.