Figure 4.
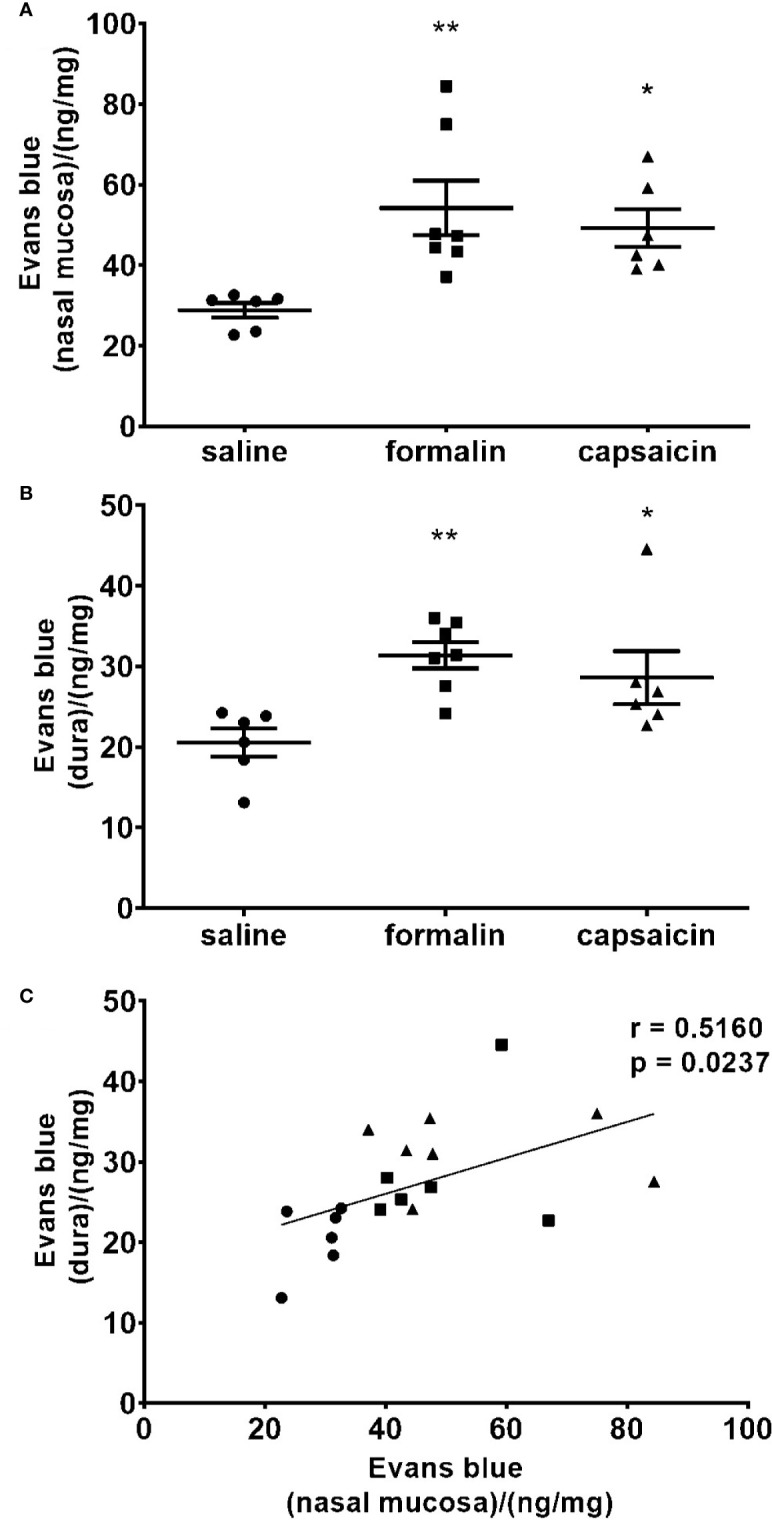
Local stimulation of the deep nasal mucosa by formalin (2.5%) or capsaicin (0.1%) induce plasma protein extravasation in the nasal mucosa and cranial dura mater. The inflammation was quantified by spectrophotometric measurement of formamide extracts of Evans blue dye (ng of the dye per mg of tissue in the nasal mucosa (A) and dura mater (B). Mean ± SEM, 6–8 animals per group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. saline-treated group (one-way ANOVA followed by Newman Keuls post hoc test). Intensity of the inflammation in nasal mucosa correlated with the intensity of inflammation in cranial dura. (C) Individual animal values are plotted showing extravasation in the nasal mucosa (horizontal axis) and dura (vertical axis) for all experimental groups together (circle, saline; square, formalin; triangle, capsaicin; r, Pearson’s correlation coefficient).
