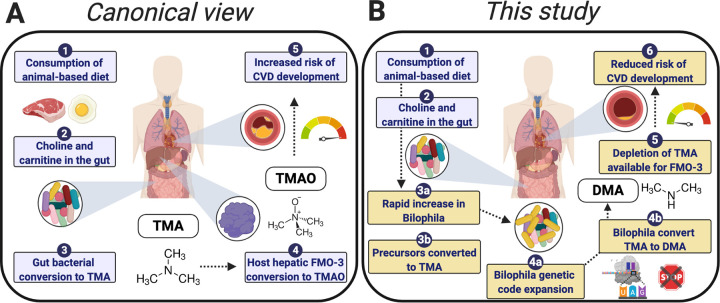
FIG 1.
(A) Canonical view of TMA: this compound is converted to TMAO in the liver via a host hepatic flavin monooxygenase 3, leading to increased risk of cardiovascular disease. (B) A new view of TMA metabolism proposed in this study: the specialized gut bacteria, Bilophila, increase in abundance and use genetic code expansion to augment metabolism, thereby reducing the amount of TMA available for conversion to TMAO. TMA, trimethylamine; FMO-3, flavin monooxygenase 3; TMAO, trimethylamine-N-oxide; CVD, cardiovascular disease; DMA, dimethylamine.