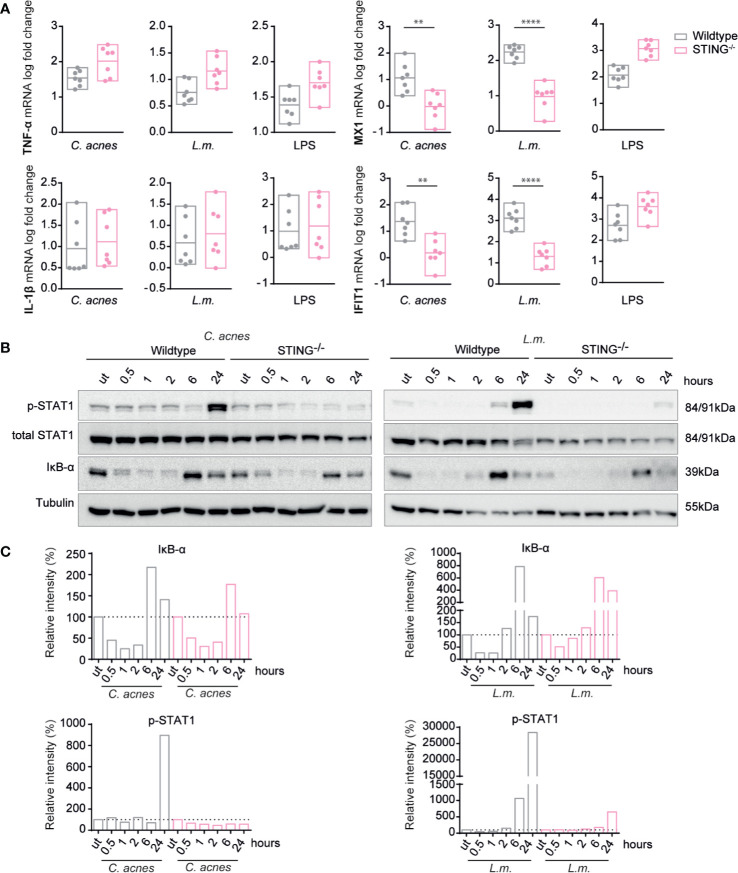
Figure 5.
Induction of innate immune signaling pathways in response to C. acnes infection in STING-deficient human macrophages. (A) Differentiated wildtype and STING-deficient THP-1 cells were infected with either C. acnes strain NCTC737, L.m. or stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 0.4µg/ml) for either 6 (TNF-α, IL-1β) or 24 h (MX1, IFIT1). HPRT-normalized gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR and shown as log transformed fold change to the uninfected sample. Data represent the mean values of seven independent experiments. P values were calculated using the unpaired t-test of log transformed values (**P ≤ 0.01; ****P ≤ 0.0001). (B) Differentiated wildtype and STING-deficient THP-1 cells were infected with either C. acnes strain NCTC737 or L.m. for indicated timepoints. Protein expression of IκB-α, total STAT1, Phospho-Y701 STAT1, and tubulin (housekeeping gene) was measured by western blot. (C) The representative blots in (B) were quantified using Image Lab. Relative intensities of the bands were normalized to their corresponding tubulin levels. Data represent relative intensities in percent to the corresponding uninfected control (equals 100%).