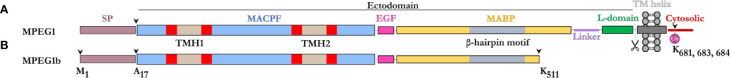
Figure 1.
Domain schematic of MPEG1 in two isoforms. (A) The majority of MPEG1 consists of a MACPF (blue) and MABP (yellow) domain. The MACPF domain contains functional motifs, namely the TMH regions (tan/red) that unfurl to form a β-barrel upon pore formation. The MABP domain contains a β-hairpin motif (gray) that recognizes and binds to negatively charged phospholipids. A small EGF-like motif (pink) is located between the MACPF and MABP domains. The MABP domain is followed by a small linker region (purple) and conformationally labile motif, denoted the L-domain (green). These directly precede the transmembrane helix (dark gray) and cytosolic (red) regions. The cytosolic region contains a lysine rich motif that is monoubiquitinated during immune response. Scissors depict the putative cleavage site of MPEG1. The majority of MPEG1 constitutes the ectodomain and is postulated to be proteolytically shed from the bilayer. (B) MPEG1b is a shorter secreted isoform that is truncated in the MABP domain at K511 (arrow). Both MPEG1 and MPEG1b are directed to the ER by a signal peptide (SP; copper rose) that is cleaved (arrow) shortly after translation.