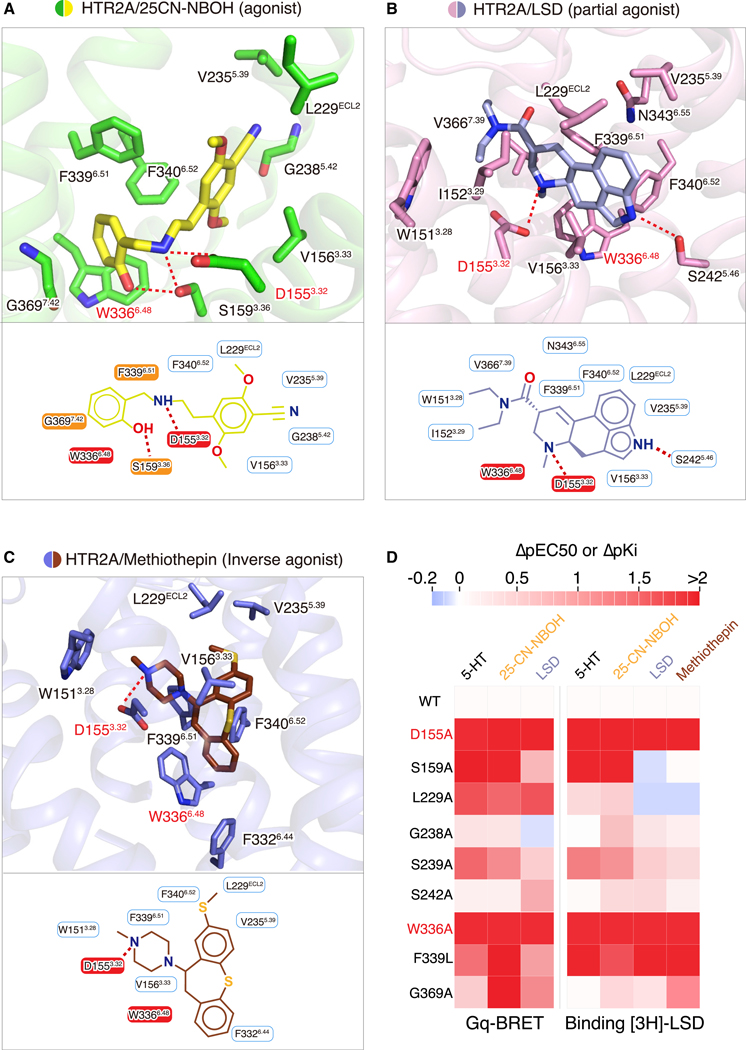
Figure 3. Ligand-Specific Interactions with HTR2A.
(A–C) Specific residues in the binding pockets that interact with 25CN-NBOH (yellow) (A), LSD (light blue) (B), and methiothepin (brown) (C), respectively. Alternative 2D diagrams showing direct interactions with each ligand are also provided at the bottom of each panel. The salt bridge interaction, as well as hydrogen bond interactions, is shown as red dashed lines.
(D) Mutagenesis studies showing the effects of orthosteric-site residues on ligand-binding affinity and functional activity. Heatmap of ΔpEC50 (EC50WT-EC50mt) (by BRET 2, HTR2A/Gαq) and ΔpKi (Kiwt-Kimt) (by binding assay, [3H]-LSD) shows differences between HTR2A wild-type and mutants. See Figure S6 and Tables S5 and S6 for fitted parameter values that represent mean ± SEM of n = 3 biological replicates.
See also Figure S5.