Fig. 3.
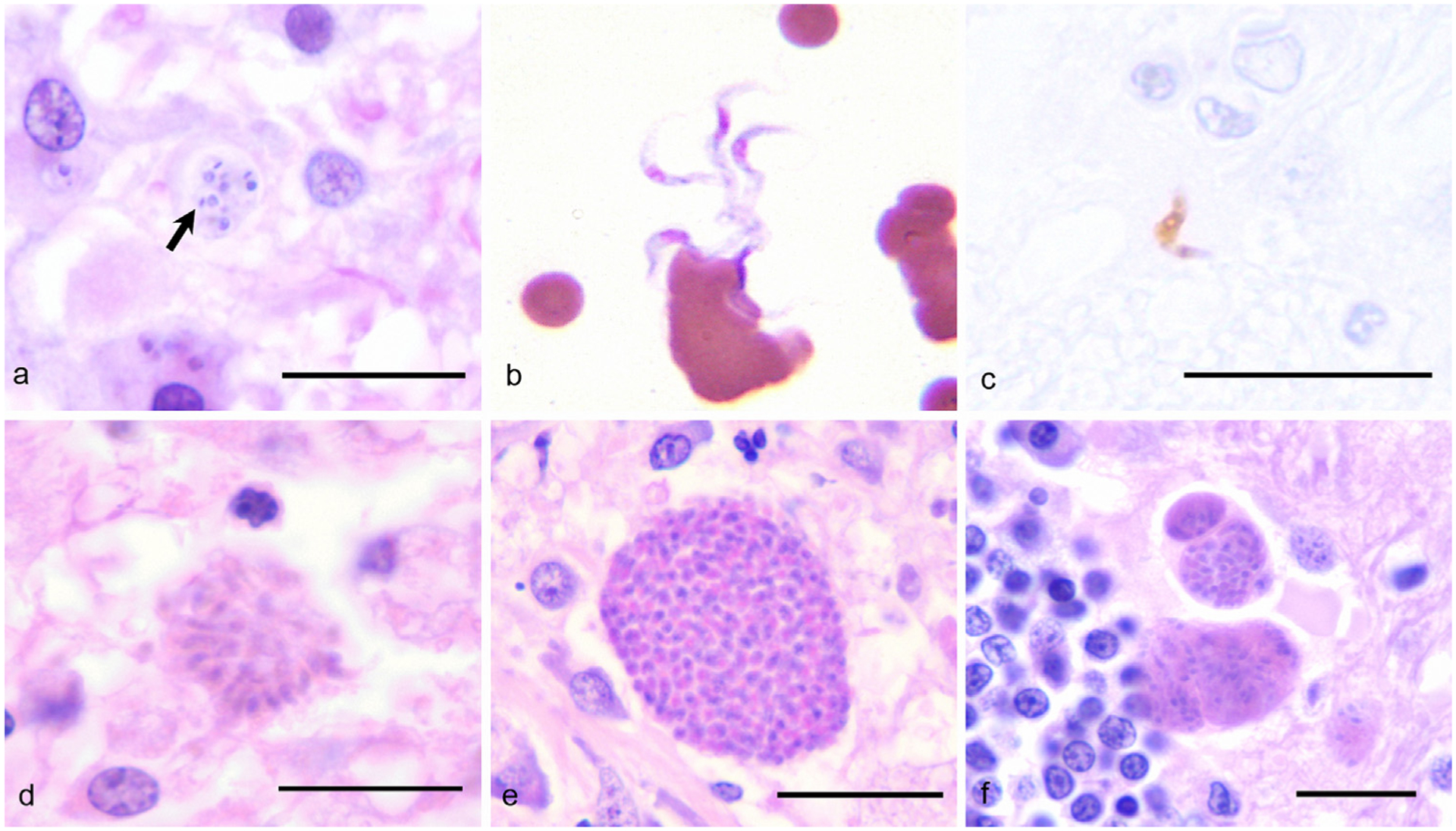
A comparison of selected protozoal agents that affect the CNS. The details of the cases in panels b and c have been previously published (Rodrigues et al., 2009), and the cases were re-photographed for this report. (a) Trypanosoma cruzi amastigotes (arrow) within the cerebrum of a dog; HE, 1000×, Bar = 10 μm. (b) Trypanosoma evansi trypomastigotes in the peripheral blood of a horse; Dif-quick, 1000×. (c) Immunohistochemistry identifies a Trypanosoma evansi trypomastigote in the brain of a horse; Avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex, 1000×, Bar = 10 μm. (d) Sarcocystis neurona merozoites within the brain of a horse; HE, 1000×, Bar = 10 μm. (e) Neospora spp. tissue cyst in the brain of a dog; HE, 1000×, Bar = 10 μm. (f) Toxoplasma gondii tissue cyst within the brain of a cat; HE, 1000×, Bar = 10 μm.
