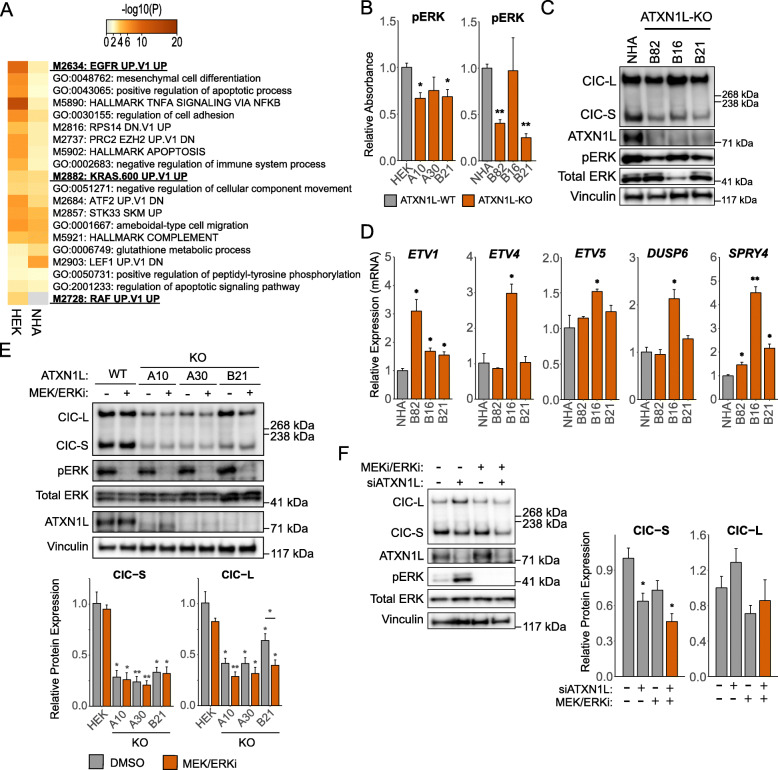
Fig. 2.
ATXN1L-mediated CIC instability is independent of ERK activity. a Heatmap showing the top 20 upregulated gene sets in ATXN1LKO NHA and HEK cell lines. Terms related to the MAPK pathway are bolded. b ELISA quantification of phosphorylated ERK (pThr202/Tyr204) in ATXN1LWT and ATXN1LKO NHA and HEK cell lines. Quantifications were normalized to total ERK. c Representative Western blot of phosphorylated ERK (pThr202/Tyr204) in ATXN1LWT (NHA) and ATXN1LKO (B82, B16, B21) cell lines. d Relative mRNA expression of CIC target genes ETV1/4/5, DUSP6, and SPRY4 in ATXN1LWT (NHA) and ATXN1LKO (B82, B16, B21) cell lines. Gene expression was normalized to TBP, and the parental ATXN1LWT (NHA) cell line was used as a relative control. e Representative Western blot of ATXN1LWT (HEK) and ATXN1LKO (A10, A30, B21) cell lines treated with MEK/ERK inhibitors trametinib/LY3214996. DMSO was used as a negative control. Below: barplot quantifications of CIC expression. Quantifications were normalized to vinculin. f Representative Western blot of ATXN1LWT (HEK) cells treated with MEK/ERK inhibitor and/or ATXN1L siRNA. DMSO and scrambled siRNA were used as negative controls. Right: barplot quantification of CIC expression. Quantifications were normalized to vinculin. Western blot, ELISA, and RT-qPCR quantifications were collected from 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent one standard deviation. p values were calculated using the two-tailed independent Student’s t test. Statistically significant values are denoted (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Individual data values can be found in Additional file 17: Table S10