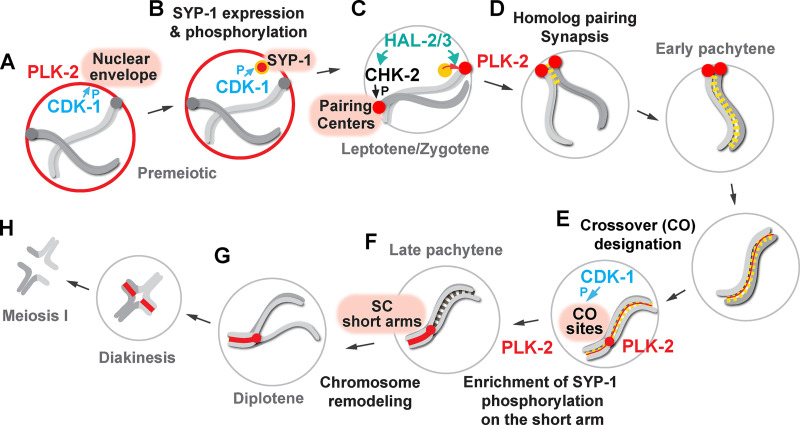
Figure 8.
Model for targeting PLK-2 to distinct subnuclear structures during meiotic prophase in C. elegans. (A) In the premeiotic region of the germline, CDK-1 primes the localization of PLK-2 to the nuclear envelope. P, phosphorylation. (B) CDK-1 phosphorylates newly expressed SYP-1 at T452 just before the meiotic onset, and a pool of PLK-2 can localize to SC polycomplexes. (C) Upon meiotic entry, CHK-2 becomes active and phosphorylates the pairing center proteins (Kim et al., 2015), which serve as the preferred docking sites for PLK-2. The nucleoplasmic HAL-2/3 complex ensures the PLK-2 localization to pairing centers by promoting CHK-2 activity and by preventing premature association of PLK-2 to SYP proteins. (D) Constrained PLK-2 activity at the pairing centers is essential for proper axis assembly, homologue pairing, and synapsis. (E) CDK-1 is also responsible for targeting PLK-2 to the crossover-designated sites. (F) SYP-1 phosphorylation and PLK-2 are enriched on the SC short arm relative to the crossover site, and this requires PLK-2 kinase activity and a threshold level of crossover within the nucleus. (G) PLK-2 drives the asymmetric SC disassembly. (H) The short arm becomes the site of cohesion loss during meiosis I.