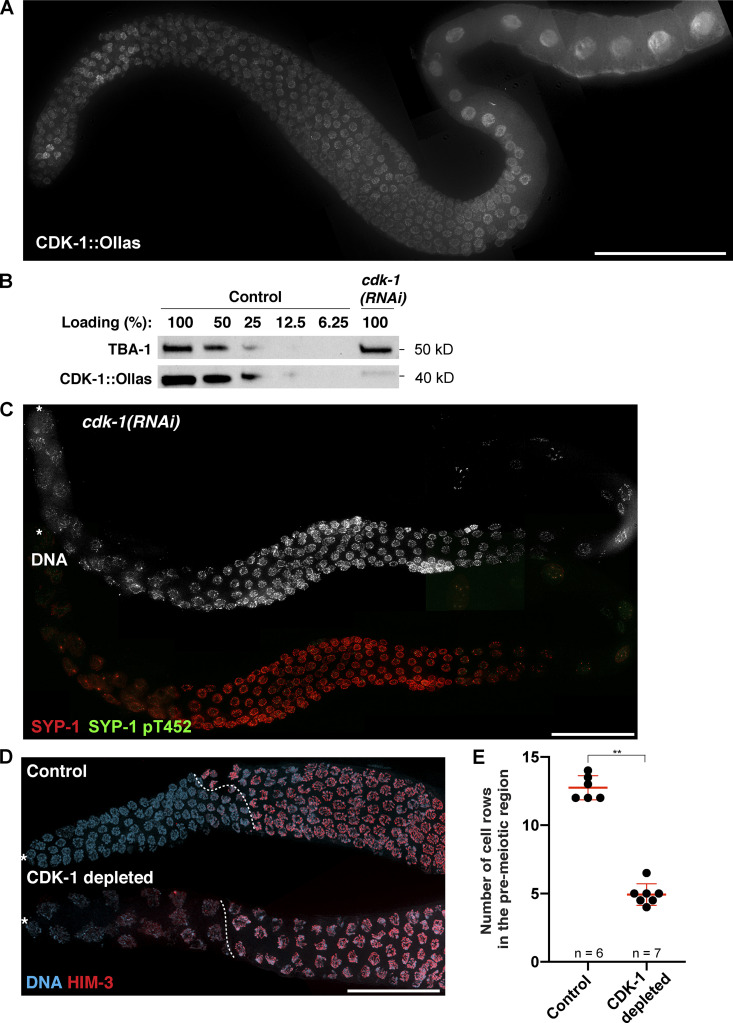
Figure S4.
Knockdown of CDK-1 by RNAi abolishes the phosphorylation of SYP-1 at T452 and abrogates PLK-2 targeting to the SC. (A) Composite immunofluorescence image of a full-length gonad dissected from a worm strain expressing CDK-1::Ollas. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Western blots showing the knockdown of CDK-1 by RNAi. The level of CDK-1::Ollas in cdk-1(RNAi) worms was compared with serially diluted worm lysates from control animals. Tubulin (TBA-1) was used as a loading control. Molecular weights for both proteins are indicated on the right. (C) Composite immunofluorescence images of a full-length gonad from a cdk-1 RNAi–treated worm showing DNA (white), SYP-1 (red), and SYP-1 pT452 staining (green). Asterisks indicate the distal tip of the germline. Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Immunofluorescence images of distal germlines from control and CDK-1–depleted animals showing DNA (blue) and HIM-3 (red) staining. Asterisks indicate the distal tip of the germline, and dotted lines indicate the meiotic entry. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Graph showing the number of cell rows in the premeiotic region in control versus CDK-1–depleted germline. Mean ± SD is shown. Numbers of gonads scored are indicated on the bottom (n = 6 for control; n = 7 for CDK-1 depleted). **, P < 0.01 by two-tailed Mann-Whitney test.