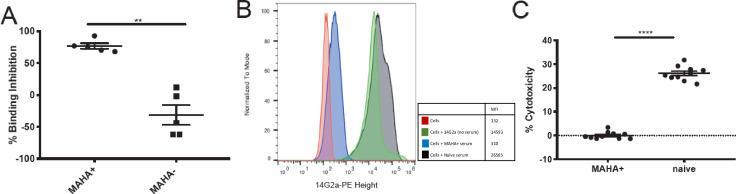
Figure 2.
Serum containing MAHA inhibits IC in vitro (A) using a binding inhibition detection ELISA; serum from MAHA+ mice or MAHA− naive serum was combined with IC prior to addition to the 1A7 coated plates. Hu14.18-IL2 bound to 1A7 was detected and the percent binding inhibition was calculated for each mouse (p=0.008, n=5 mice per group in each experiment; two replicate experiments were performed, one replicate shown); each dot represents one individual sample, with group mean and SE of the mean shown. Non-parametric t-tests were performed. (B) Human M21 melanoma cells were incubated with a mixture of MAHA+ or MAHA− serum and 14G2a-PE antibody. The Median Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) of 14G2a-PE in the presence of MAHA+ or MAHA− serum was detected by flow cytometry; the binding histograms for a single representative mouse are shown. (C) The cell-mediated cytotoxicity of IC, in an ADCC assay, in the presence of MAHA+ versus MAHA− serum, was determined (p<0.0001). IC concentration of 20 ng/mL was chosen after testing multiple concentrations of IC without serum (not shown). Two separate human effectors were used. Results from one of two replicates are shown with an effector to target ratio of 40:1; total n=40. Welch’s t-test was used to compare groups. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001. ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular-mediated cytotoxicity; IC, immunocytokine; MAHA, mouse anti-human antibody.