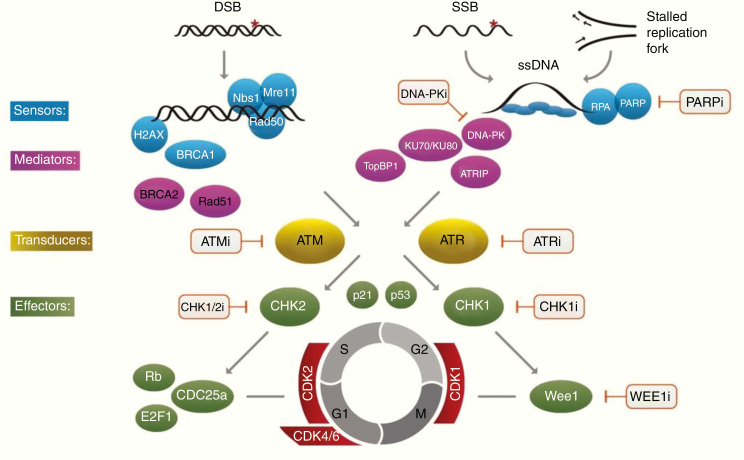
Fig. 11.
A simplified overview of signaling from common types of DNA damage to the DDR and cell cycle checkpoint pathways. Initial damage is sensed by proteins including the histone γ -H2AX, which is rapidly phosphorylated by ATM at a specific serine residue in response to chromatin structure alteration at DBS sites, activating recruitment of repair proteins including BRCA1 and the MRN complex (MRE11, Rad51, NBS1). DSB repair is undertaken by the end-joining pathway involving the kinase DNA-PK and Ku protein binding partners and the homologous recombination pathway involving Rad51 and associated proteins. Single strand breaks (SSB) and replication stress leading to stalled replication forks activate PARP which in turn recruits repair factors including XRCC1 and promotes chromatin remodeling at the break site and base excision repair. ATR and ATM function both in the initial signaling cascade and as transducers to downstream activation of the cell cycle checkpoints inhibitors, Chk1 and Chk2 producing cell cycle delay to facilitate repair. Points in the pathway at which specific inhibitors are available are indicated. As predicted from their roles in the DDR pathway, ATM and ATR inhibitors sensitize to a broad range of DNA damaging agents causing single or double strand breaks. PARPi and cell cycle checkpoint inhibitors including Wee1 inhibitors are specifically effective in cells undergoing rapid replication. DSB = Double Strand Break; SSB = Single Strand Break.