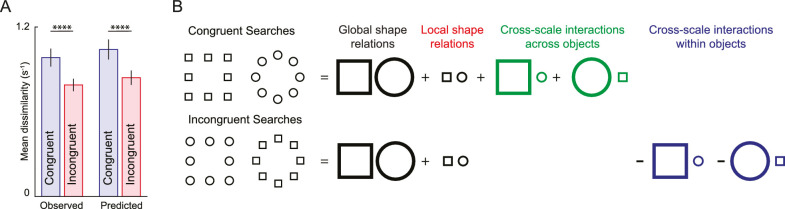
Figure 6.
Incongruence effect in visual search. (A) Average dissimilarity for congruent and incongruent image pairs for observed dissimilarities (left) and dissimilarities predicted by the multiscale part sum model (right). Error bars indicate SD across image pairs. Asterisks indicate statistical significance, as calculated using an ANOVA, with conventions as before. (B) Schematic illustrating how the multiscale model predicts the incongruence effect. For both congruent and incongruent searches, the contribution of global and local terms in the model is identical. However, for congruent searches, the net dissimilarity is large because cross-scale across terms are non-zero and within-object terms are zero (because the same shape is present at both scales). In contrast, for incongruent searches, the net dissimilarity is small because across-object terms are zero (since the local shape of one is the global shape of the other) and within-object terms are non-zero and negative.