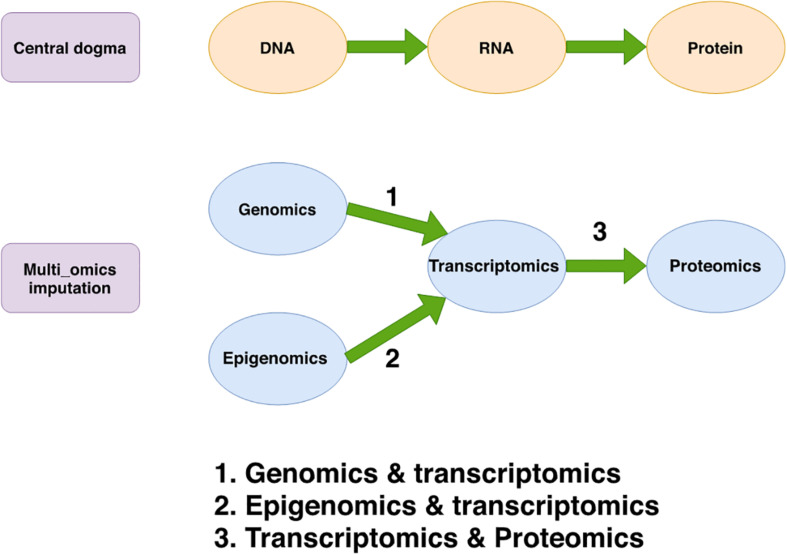
FIGURE 1.
The genetic information flow from DNA to protein via RNA and the interaction between transcriptomics and genomics, epigenomics or proteomics in multi-omics data imputation. The top diagram shows the central dogma of molecular biology in which DNA is transcribed to RNA and then translated to proteins. The bottom diagram shows the integrative relationship between the genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics and proteomics datasets on which multi-omics data imputation methods are based. These methods are built by combining different omics datasets to perform integrative imputation of missing values. This is shown here by using arrows numbered by the type of data combination they represent. For example, arrow 1 shows that multi-omics imputation can be facilitated by leveraging the correlation between data from both genomics (such as SNP) and transcriptomics (such as gene expression).