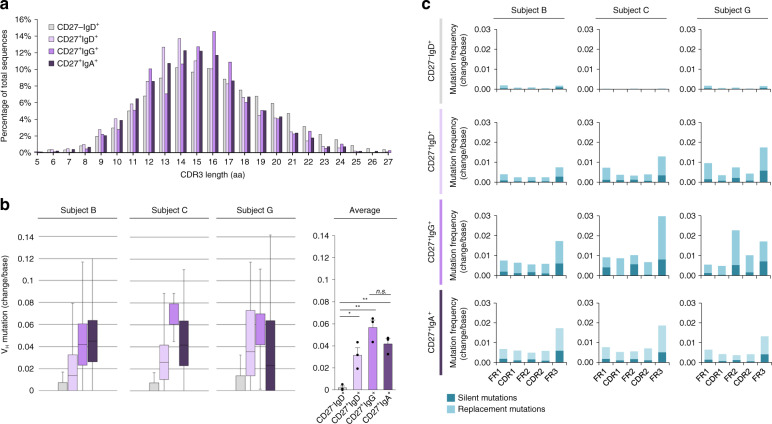
Fig. 3. CDR3 lengths and somatic point-mutations in recombined Ig VHDJH gene segments of human MBCs.
a Average percentage of total sequences at any given CDR3 length in recombined VHDJH transcripts expressed by CD27–IgD+, CD27+IgD+, CD27+IgG+, and CD27+IgA+ B cells. b Somatic point-mutations in recombined Ig VHDJH transcripts expressed by CD27–IgD+ (4302 transcripts), CD27+IgD+ (4705 transcripts), CD27+IgG+ (1564 transcripts), and CD27+IgA+ (13,549 transcripts) B cells with boxplots depicting the frequencies of point-mutations (change/base). Data are represented as boxplots where the middle line is the median, the lower and upper hinges correspond to the first and third quartiles, the upper whisker extends from the hinge to the largest value no further than 1.5 × IQR from the hinge (where IQR is the inter-quartile range) and the lower whisker extends from the hinge to the smallest value at most 1.5 × IQR of the hinge. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns not significant (paired two-sided t-test). c Frequency of silent and replacement point-mutations in framework regions (FR) and complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) in all four sorted B cell subsets for each of the three healthy human subjects. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. B cell subsets are repeated at the bottom, left to right in CD27−IgD+ (gray), CD27+IgD+ (lavender), CD27+IgG+ (purple), and CD27+IgA+ (dark purple).