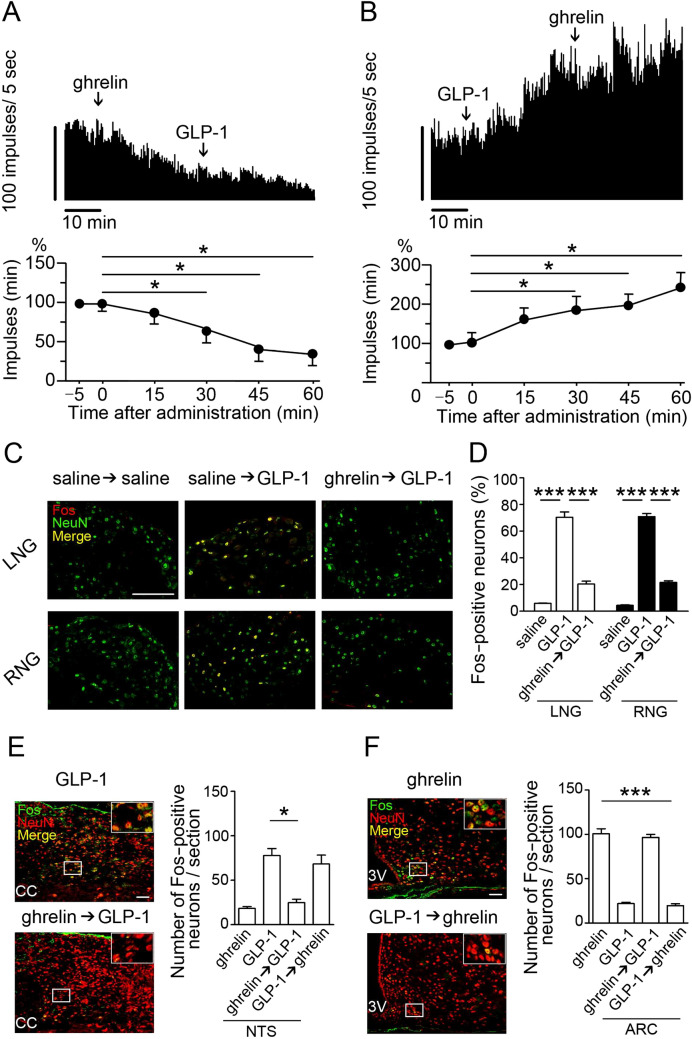
Figure 3.
Interactive roles of ghrelin and GLP-1 on the vagal afferent nerve activity and Fos expression in NG, NTS, and hypothalamic ARC. (A) Representative records of gastric vagal afferent discharge rates in the upper panel. GLP-1 administration after ghrelin to rats did not activate gastric vagal afferent activity (n = 3). (B) Ghrelin administration after GLP-1 to rats did not attenuate gastric vagal afferent activity (n = 3). (C) Representative fluorescence images of GLP-1-induced Fos expression (red) in the NG neurons (green) in response to the saline, GLP-1 and GLP-1 after ghrelin in mice (n = 3). (D) Average percentage of Fos-positive neurons in LNG and RNG. GLP-1 induced Fos expression in the NG neurons. Ghrelin preadministration 30 min before GLP-1 significantly attenuated GLP-1-induced Fos expression in the NG neurons. (E,F) Representative fluorescence images of GLP-1- or ghrelin-induced Fos expression (green) in the NTS (E) and ARC (F) neurons (red). Ghrelin preadministration 30 min before GLP-1 significantly attenuated GLP-1-induced Fos expression in the NTS. GLP-1 preadministration 30 min before ghrelin significantly attenuated ghrelin-induced Fos expression in the ARC (n = 4). Magnified photographs represent Fos expression in the neurons (yellow in white box). CC, central canal; 3 V, third ventricle. Scale bars (C,E), 50 µm. All values are means ± SE. ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05.