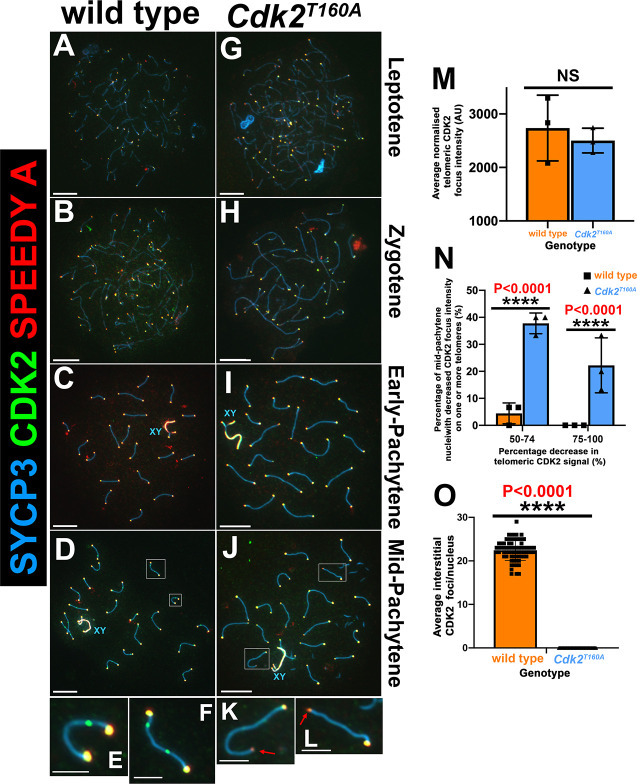
Fig 3. CDK2/Speedy A localization in Cdk2T160A spermatocytes.
Chromosome spread preparations from adult (postnatal day 40) testes immunostained with CDK2 (green) and Speedy A (red) in conjunction with SYCP3 (blue) are shown for WT (A–D) and Cdk2T160A (G–J) spermatocytes for selected stages of meiotic prophase I. CDK2 and Speedy A can be detected as colocalized foci at all telomeric ends for all meiotic stages in WT (A–D and insets E–F) and Cdk2T160A spermatocytes (G–J and insets K–L). Interstitial CDK2 foci—absent of Speedy A positivity—marking LRNs are transiently observed in mid-pachytene–stage WT (D) and insets (E–F), but not Cdk2T160A spermatocytes (J and insets K, L). X–Y bivalents (blue XY labels) were also found to be positive for both CDK2 and Speedy A from early-pachytene onwards in both genotypes. All images are representative of at least 20 images taken for specified stages. Similar staining patterns were confirmed in at least 3 biological replicates. In all main panels, scale bars are representative of 5 μm; in all inset pictures, scale bars are representative of 1.25 μm. Interstitial CDK2 foci (M) were quantified specifically for mid-pachytene stages by counting the average numbers of nontelomeric CDK2 foci counted per nucleus. Data are presented as individual foci counts for WT (orange bars, N = 72) and Cdk2T160A (blue bars, N = 50); error bars are indicative of the mean and SD. For mid-pachytene, Cdk2T160A spermatocytes (J) with decreased CDK2/Speedy A signal in a subset of nuclei was observed (as marked by red arrows in insets K, L). The average telomeric CDK2 focus intensity/nuclei were quantified specifically for mid-pachytene stages (N). Data are presented as a mean intensity in AU ± SD determined from 3 biological replicates (N = 48 overall nuclei counted for WT (orange bars) and N = 48 overall nuclei counted (blue bars) for Cdk2T160A. Telomeric signals were only counted from autosomes and were excluded if involved in telomeric fusion events. All intensity values calculated for a single nucleus were normalized to the background intensity of that nuclei. Percentages of mid-pachytene–stage nuclei with at least one telomere showing a decrease in telomeric CDK2 intensity of ≥50% (as compared with the average telomeric CDK2 intensity for that cell) are quantified in panel O. Individual data used to make panel O are shown in S3G Fig. All data were assumed to be non-normally distributed. Statistical significance between genotypes was determined by unpaired t test. Significance and P-values are reported directly over each comparison. The underlying data for (M, N, O) can be found in S1 Data. AU, arbitrary unit; CDK2, cyclin-dependent kinase 2; LRN, late recombination nodule; SD, standard deviation; SYCP, synaptonemal complex protein; WT, wild-type.