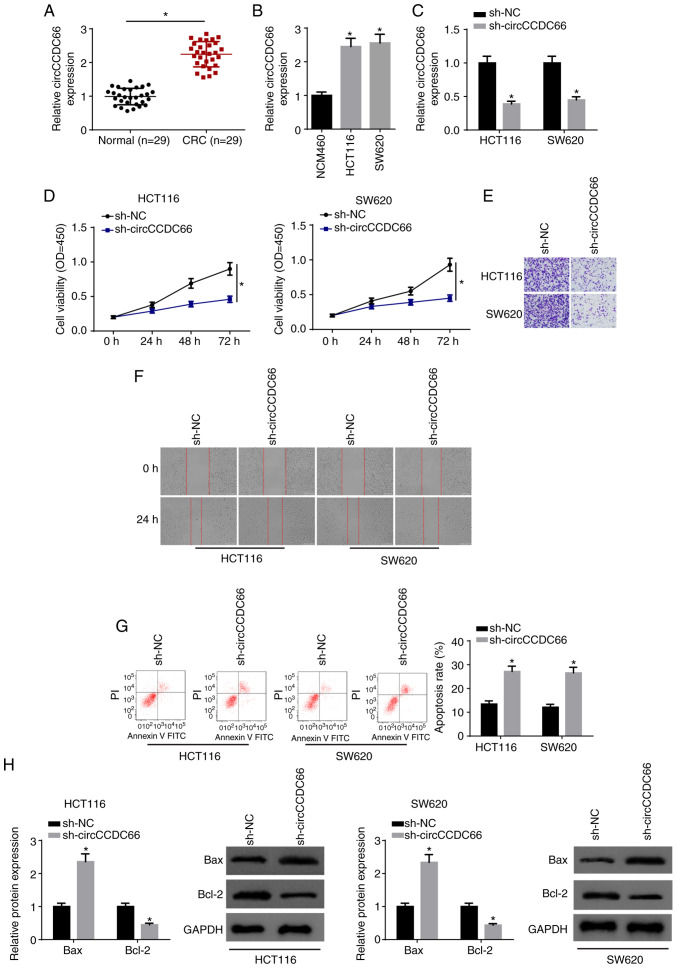
Figure 1.
Knockdown of circCCDC66 inhibits the progression of CRC cells. (A) The expression of circCCDC66 in CRC tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues was determined by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05 vs. the normal tissues. (B) Expression of circCCDC66 in CRC cell lines (HCT116 and SW620) and human colon mucosal cells (NCM460) was measured by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05 vs. NCM460 cells. (C) Expression of circCCDC66 in HCT116 and SW620 transfected with sh-NC or sh-circCCDC66 was determined by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05 vs. the sh-NC group. (D) CCK-8 assay showed the viability of HCT116 and SW620 cells transfected with sh-NC or sh-circCCDC66. *P<0.05 vs. the sh-NC group. (E and F) Transwell assay and wound healing assay were employed to determine the migratory and invasive abilities of HCT116 and SW620 cells transfected with sh-NC or sh-circCCDC66. (G) Flow cytometry analysis was used to detect the apoptosis of HCT116 and SW620 cells transfected with sh-NC or sh-circCCDC66. *P<0.05 vs. the sh-NC group. (H) The protein levels of Bax and Bcl-2 in HCT116 and SW620 cells transfected with sh-NC or sh-circCCDC66 were detected by western blot analysis. *P<0.05 vs. the sh-NC group. CRC, colorectal cancer.