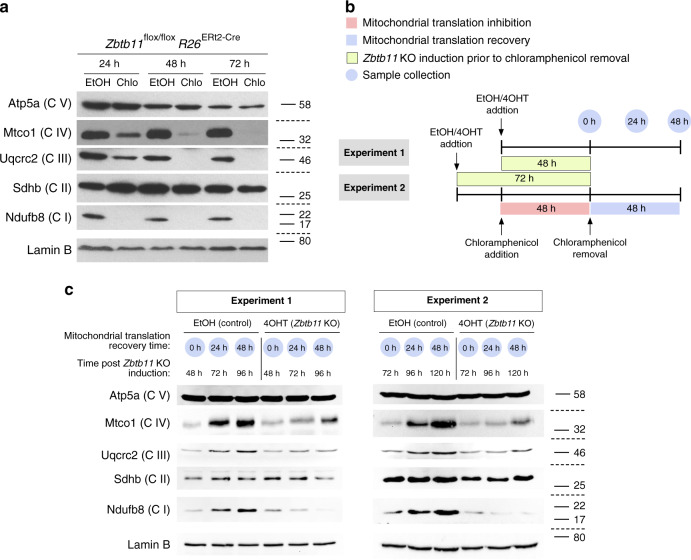
Fig. 7. Zbtb11 is required for the biogenesis of respiratory complexes I, III and IV.
a SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting of whole-cell extracts following inhibition of mitochondrial translation with chloramphenicol. Samples from cells treated with ethanol (carrier) were used as reference. Note that complexes I, III and IV are sensitive to the mitochondrial translation block. Lamin B is shown as a loading control. Molecular weight marker unit is kDa. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b Diagram of the experimental design used to compare de novo synthesis of respiratory complexes in control and Zbtb11 KO cells. Fully assembled complexes I, III and IV were depleted from Zbtb11lox/lox Rosa26ERt2-Cre cells by inhibiting mitochondrial translation for 48 h (as in a). Mitochondrial translation was then allowed to resume by removing the chloramphenicol treatment, and samples for immunoblotting were collected at 24 h intervals in order to monitor the regeneration of respiratory complexes. The chloramphenicol treatment was synchronised with the addition of 4OHT (or EtOH as control), so that translation was allowed to resume either 48 h (experiment version 1) or 72 h (experiment version 2) post Zbtb11 KO induction, thus allowing to compare de novo synthesis of respiratory complexes in control and Zbtb11 KO cells. c Immunoblotting analyses of representative experiments comparing de novo synthesis of respiratory complexes I, III and IV, in control and Zbtb11 KO cells, as outlined in b. Molecular weight marker unit is kDa. Note that the synthesis of complexes III and IV is only partly impaired in Zbtb11 KO cells, while the synthesis of complex I is completely blocked. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.