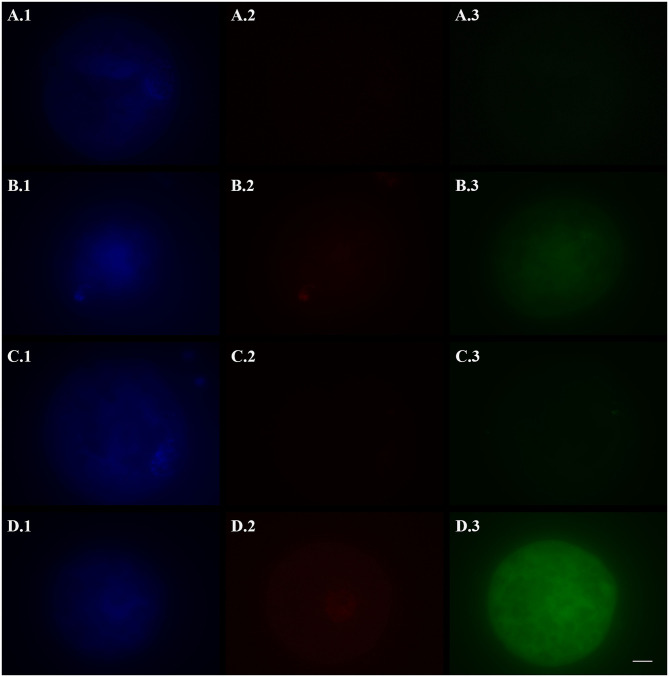
Figure 1.
Representative fluorescence micrographs of vitrified (A,B), fresh (C, negative control), and hydrogen peroxide-treated (D, positive control) domestic cat oocytes stained with Hoechst 33342 (1), TUNEL assay (2), and a caspase activity assay (3) to assess the activation of apoptotic pathways. Vitrified oocytes were stained 2 (A) or 24 (B) h after warming. Bright blue fluorescence (A.1,B.1,C.1,D.1) indicates the nuclear material. Bright red fluorescence (B.2,D.2) in the nuclear area indicates DNA fragmentation by TUNEL assay. Green fluorescence in the ooplasm (A.3,B.3,C.3,D.3) indicates, according to its intensity, the extent of caspase activity. Images were captured in black and white and pseudo-colored after acquisition with the Imaging Software ZEN 2.5 blue edition. Black and white balance of Hoechst (1) and TUNEL (2) images was adjusted after coloring to make nuclear stainings more visible in print. Caspase images, which were used for quantification, were not modified. Scale bar: 20 μm.