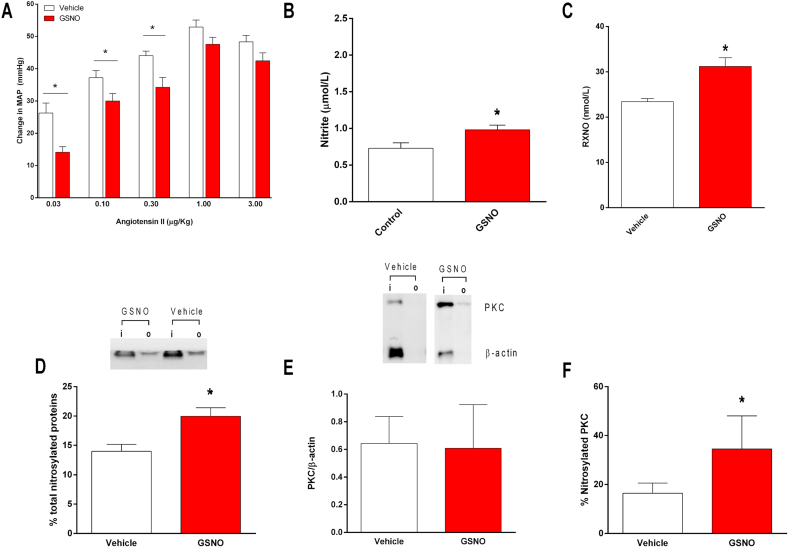
Fig. 3.
Pretreatment with S-nitrosogluthatione (GSNO) increases the concentrations of nitrosylated species (RXNO) in plasma, enhances total protein and PKC nitrosylation in the vessels and attenuates the blood pressure responses to angiotensin II in vivo. Panel A shows the increases in mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) after infusion of angiotensin II (0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0 and 3.0 μg/kg, i.v.) in rats pretreated with oral GSNO (0.2 mmol/kg) or vehicle for five days. Panels B and C show the concentrations of nitrite and nitrosylated species (RXNO), respectively, in plasma from rats pretreated with oral GSNO or vehicle. Panel D shows a representative SDS/PAGE gel stained with Coomassie Blue to quantify total protein nitrosylation in aortic samples from GSNO or vehicle-treated animals using the SNO-RAC method (“I” corresponds to input: total protein; “o” corresponds to output: nitrosylated protein). The bar graphic shows the quantification of total nitrosylated proteins in the aortic samples. Panel E shows the quantification of PKC expression in the aortas using Western blotting analysis and show a representative marking to quantify PKC nitrosylation. Panel F show the quantification of PKC nitrosylation in aortic samples from GSNO or vehicle-treated animals. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5–10/group). *P < 0.05 versus Vehicle. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)