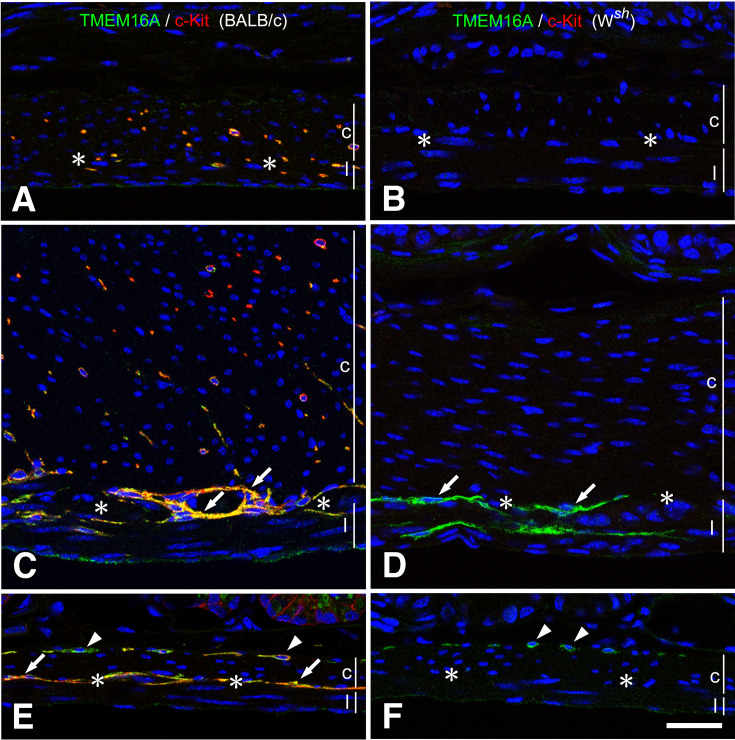
Fig. 1.
Musculature of the stomach and small intestine of BALB/c and Wsh/Wsh mice.
ICC were detected using immunofluorescence, showing TMEM16A immunoreactivity (green) and c-Kit ACK4 immunoreactivity (red) in both BALB/c (A, C, E) and Wsh/Wsh (B, D, F) mice. In the fundus (A, B), ICC-IM were observed in the musculature only in BALB/c mice. In the corpus (C, D), BALB/c mice have ICC-MY (arrows) and ICC-IM. Contrastingly, Wsh/Wsh mice have only ICC-MY (arrows) that were confirmed through TMEM16A immunoreactivity. In the small intestine (E, F), BALB/c mice have ICC-DMP (arrowheads) and ICC-MY (arrows) with TMEM16A (green) and c-Kit (red) immunoreactivities, whereas Wsh/Wsh mice have TMEM16A immunopositive ICC-DMP (arrowheads) in the circular muscle. c and l represent circular and longitudinal muscle layers, respectively. Asterisks show myenteric layer. Bar: 50 μm.