Fig. 2. A GAP + R6 ML model including long-range dispersion.
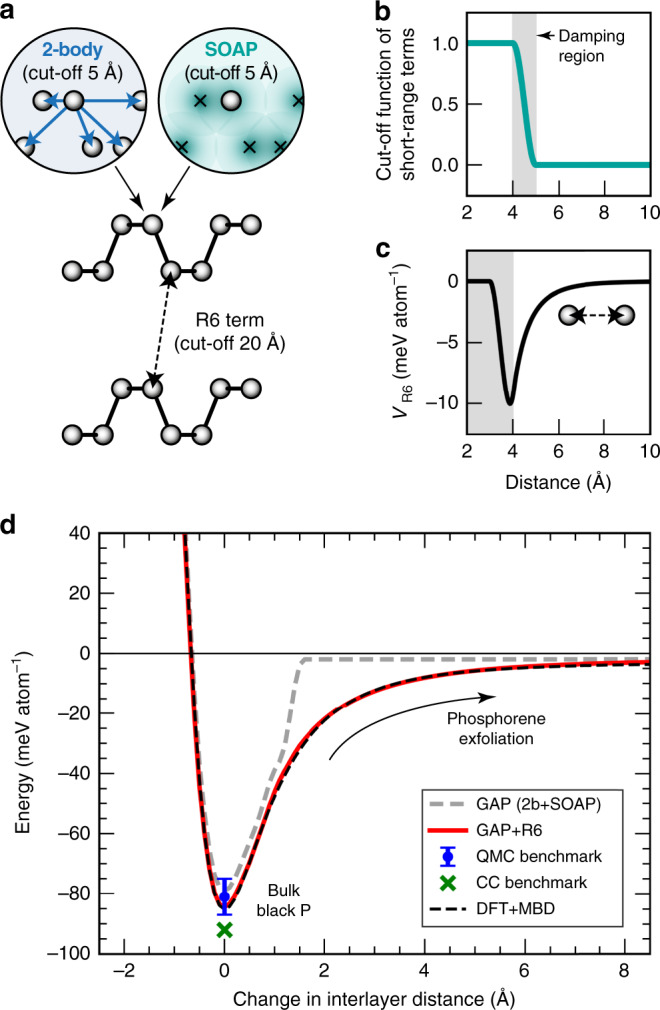
a Schematic sketch of the different types of structural descriptors, here illustrated for a pair of partially exfoliated phosphorene sheets—emphasising the medium-range (5 Å) and long-range (20 Å) descriptors that are combined in our approach (“Methods” section)68. b, c Modelling the different length scales: the upper panel shows the cut-off function used to bring the 2-body and SOAP descriptors smoothly to zero between 4 and 5 Å; the lower panel shows the long-range term, VR6, evaluated for an isolated pair of atoms in the absence of the ML terms. d Phosphorene exfoliation curve from our GAP + R6 model (red) compared to the DFT + MBD reference (dashed black line), giving the energy computed for black P (structure from ref. 70) as a function of the interlayer distance. A GAP fit without the long-range “+R6” term, i.e., based only on a 2b+SOAP fit with a 5-Å cut-off, is included for comparison (dashed grey line). To obtain these curves, the sheets have been shifted along the [010] direction without further relaxation, and the energy is referenced to that of a free monolayer. Benchmark results for the exfoliation energy from quantum Monte Carlo (QMC, −81 ± 6 meV/atom, with bars showing the error given by the authors, ref. 31) and coupled-cluster (CC, −92 meV/atom, ref. 32) studies are given by symbols, both plotted at the horizontal zero.
