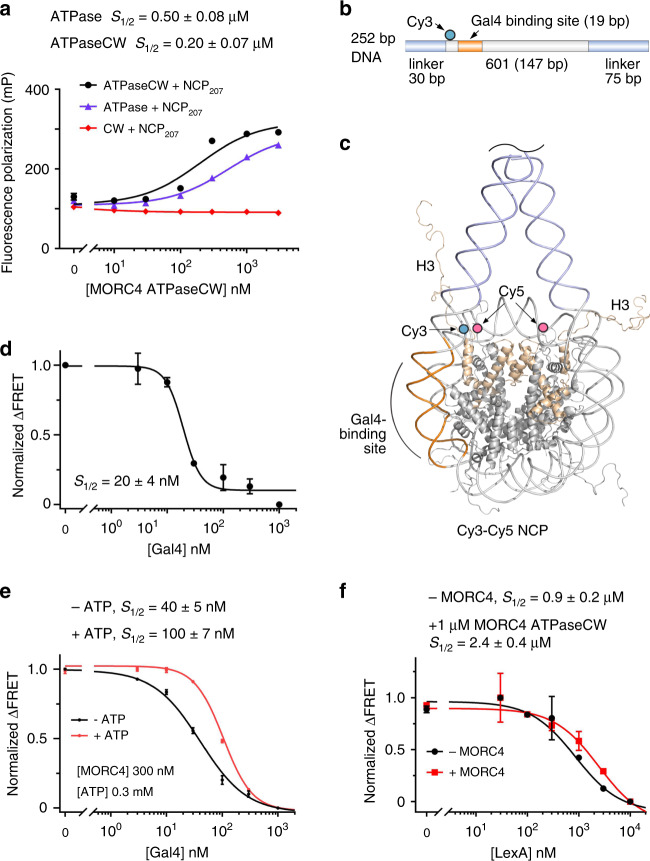
Fig. 6. MORC4 ATPaseCW binds to and stabilizes nucleosomes.
a Binding affinities and binding curves for the interactions of the indicated MORC4 regions with NCP207 as measured by fluorescence polarization. Data are represented as mean values +/− S.D. from three independent experiments (n = 3). b Schematic of the 252 bp DNA containing the 601 Widom sequence with a 75 bp linker at the 3′ end, a 30 bp linker at the 5′ end, and a Gal4 transcription factor binding site at bases 8–26 in the 601 Widom sequence with Cy3 positioned 34 bp from the 5′ end (cyan circle). c A model based on the crystal structure of the NCP with 197 bp palindromic 601 L DNA (PDB ID: 5NL0, the linker histone H1 is not shown) with histone H3 (wheat), Cy5 at H2AK119C (pink circles), Cy3 at the DNA (cyan circle), and the Gal4 target site (orange) are shown and labeled. Truncated DNA linkers are shown and colored light blue. d, e Normalized change in FRET efficiency of the Cy3-Cy5 labeled NCP252 upon addition of Gal4 in the absence (d) and presence (e) of MORC4 ATPaseCW and +/−ATP. Data are represented as mean values +/− S.D. from three independent experiments (n = 3). f Normalized change in FRET efficiency of the Cy3-Cy5 labeled NCP147 upon the addition of LexA in the absence and presence of MORC4 ATPaseCW. Data are represented as mean values +/− S.D. from three independent experiments (n = 3).