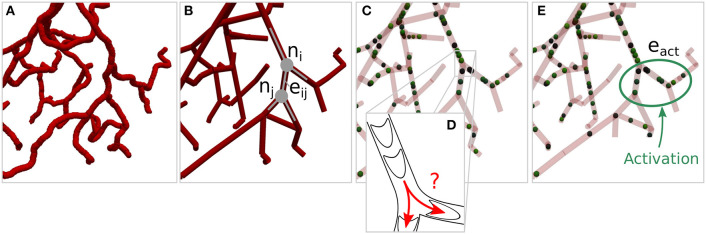
Figure 1.
Network representation of a realistic microvascular network and visualization of the tracking of individual red blood cells. (A) Tortuous structure of a realistic microvascular network. (B) Corresponding network consisting of nodes and edges. The blood vessels are represented by straight pipes. (C) Individual red blood cells that follow the flow field and dynamically affect the flow resistance in the network. (D) Schematic of red blood cells squeezing through the vessels and bifurcation rule. (E) Example of a set of activated edges in which the average perfusion will be increased, i.e., where a target flow rate is prescribed, in response to diameter adaptations.