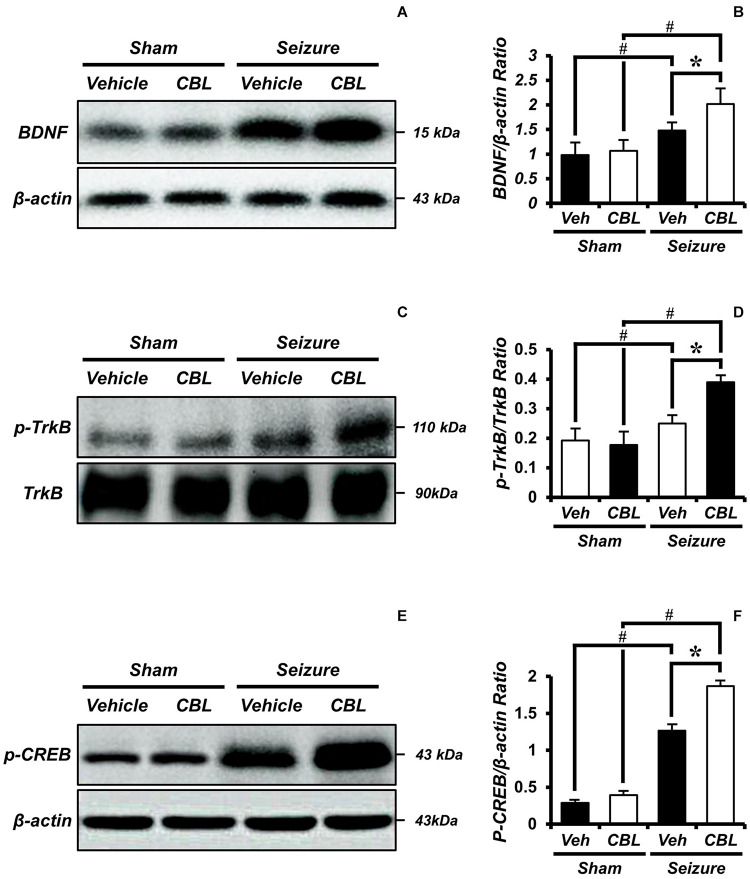
FIGURE 6.
Cerebrolysin increases the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), phospho-tyrosine kinase receptor B (p-TrkB), and phospho-cAMP-response-element-binding (p-CREB) after pilocarpine-induced seizure. The administration of cerebrolysin increased BDNF after pilocarpine-induced seizure. (A) The level of BDNF in the hippocampus. After a seizure, the administration of cerebrolysin increased BDNF expression in the hippocampus compared to the seizure-vehicle groups. (B) A graph of the BDNF. (C) The level of p-TrkB in the hippocampus. After a seizure, the administration of cerebrolysin increased p-TrkB expression in the hippocampus compared to the seizure-vehicle groups. (D) A graph of the p-TrkB. (E) The level of p-CREB in the hippocampus. After a seizure, the administration of cerebrolysin increased p-CREB expression in the hippocampus compared to the vehicle groups. (F) A graph of the p-CREB. The data are the mean ± SEM, n = 3–4, for each seizure group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group; #p < 0.05 vs. sham-operated group [Kruskal–Wallis test with post hoc test: (B) Chi square = 9.705, df = 3, p = 0.021, (D) Chi square = 9.029, df = 3, p = 0.029, (F) Chi square = 11.895, df = 3, p = 0.008].