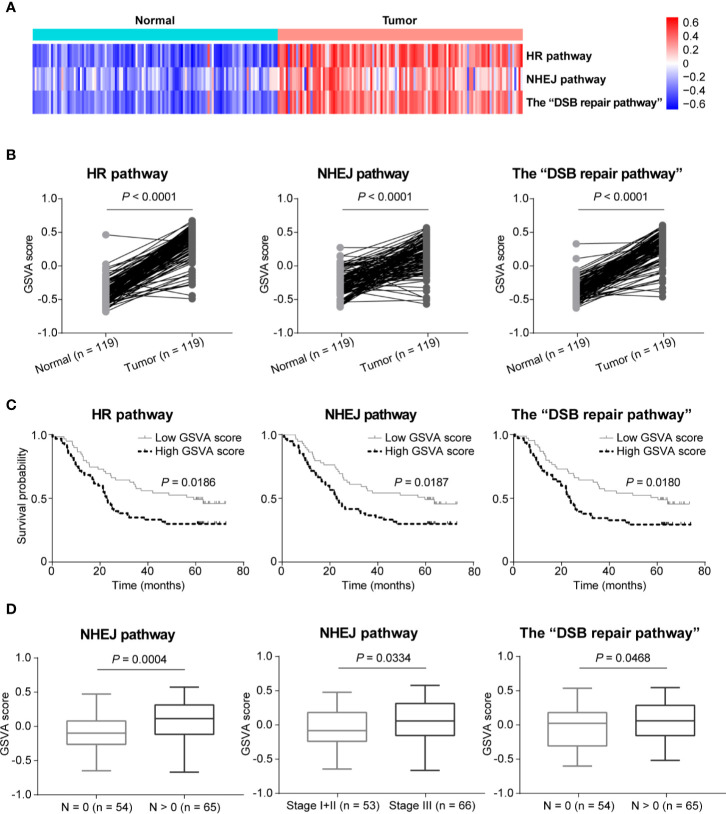
Figure 5.
The activities of double-strand break (DSB) repair pathways were up-regulated in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC) as determined by gene set variation analysis (GSVA). (A) A heatmap that shows the GSVA scores of homologous recombination (HR), non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), and the “DSB repair pathway” in each ESCC or normal sample. (B) Welch’s unequal variances t-test result showed that the activities of HR, NHEJ and the “DSB repair pathway” were significantly up-regulated in ESCC based on the GSVA scores. ESCC patients were divided into two groups based on the median GSVA scores of HR, NHEJ and the “DSB repair pathway” respectively, and survival analysis was then performed. High activities of HR, NHEJ, and the “DSB repair pathway” were associated with shorter overall survival (C). (D) Compared to ESCC patients with N = 0, the GSVA scores of NHEJ and the “DSB repair pathway” were significantly higher in ESCC cases with N > 0. Besides, the GSVA scores of NHEJ in ESCC samples of stage III were significantly higher than ESCC patients of stage I and II.