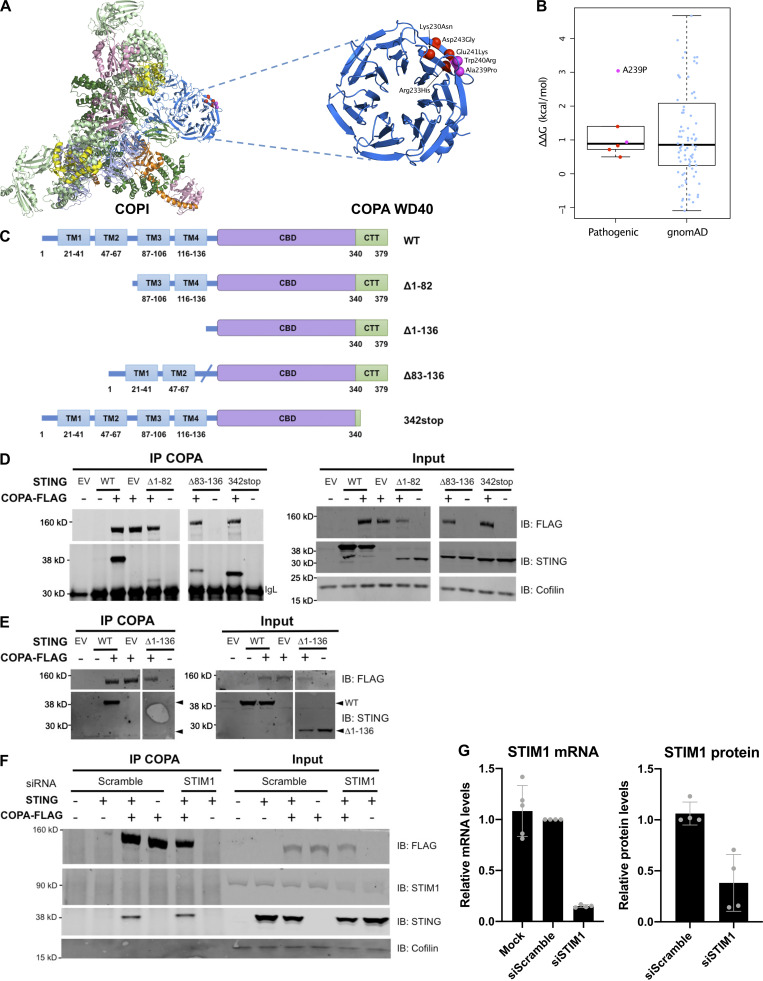
Figure S3.
COPI complex and physical interaction of COPA and STING. (A) Location of pathogenic COPA mutations within the structure of the COPI coat leaf (PDB ID: 5NZR). The four mutations from this study are shown in red, and two previously reported mutations are shown in magenta. (B) Predicted effects of pathogenic mutations and putatively benign substitutions present in the gnomAD database on protein stability, calculated with FoldX. (C) Schematic representation of WT STING and truncated STING plasmids (i.e., Δ1-82, Δ83-136, Δ1-136, and 342stop). (D) Western blot analysis of FLAG, STING, and Cofilin in proteins IP with an antibody against FLAG (IP COPA), and whole-cell lysates (input) of HEK293T cells cotransfected with EV (EV or −), or WT COPA and WT STING, or truncated STING plasmids, i.e., Δ1-82, Δ83-136, and 342stop (data representative of three independent experiments). (E) Western blot analysis as in F of proteins IP with an antibody against FLAG (IP COPA), and whole-cell lysates (input) of HEK293T cells cotransfected with EV (EV or −), or WT COPA and WT STING, STING Δ1-136 (data representative of two independent experiments). (F) Western blot analysis of FLAG, STING, STIM1, and Cofilin in proteins IP with an antibody against FLAG and in whole-cell lysates (input) of HEK293T cells cotransfected with EV (−) or WT STING and WT COPA plasmids and with a scrambled siRNA or an siRNA pool targeting STIM1. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (G) Quantification of STIM1 silencing assessed by mRNA (left) and protein (right) levels measured, respectively, by RT-qPCR and Western blot 72 h after transfection. Error bars represent SDs. Results are representative of three independent experiments. CTT, C-terminal tail.