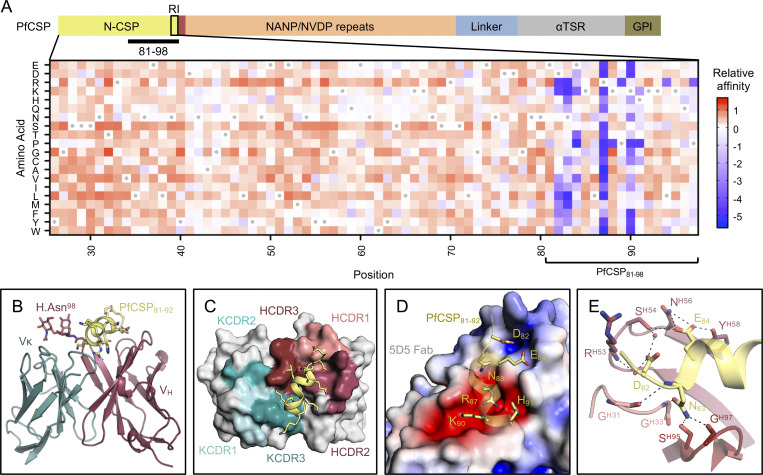
Figure 1.
Molecular delineation of the mAb 5D5 epitope in PfCSP. (A) Top: Schematic depicting the protein domain organization of PfCSP, shown with the approximate location of RI indicated by the black box and the junctional epitope represented by a dark red band. An approximate representation of PfCSP81–98 is illustrated by the black bar (not shown to scale). Bottom: Heatmap of mAb 5D5 binding affinity for N-CSP single-point mutant library. N-CSP residues included in PfCSP81–98 are indicated by the bracket at the bottom. The relative binding affinity is indicated by a diverging color scale from red to blue, where red indicates a similar affinity while blue indicates decreased affinity. The x axis denotes the N-CSP residue position, and the y axis specifies the introduced single-point mutations. Residues corresponding to the WT sequence are indicated by the gray dots. (B) Crystal structure showing the 5D5 Fab variable regions (heavy chain shown in red and κ light chain shown in blue) bound to PfCSP N-terminal residues 81–92 (yellow), which are recognized in an α-helical conformation. The N-linked glycan on H.Asn98 of 5D5 Fab is represented as sticks. (C) mAb 5D5 CDRs contacting PfCSP. HCDRs 1, 2, and 3 (salmon, raspberry, and firebrick red, respectively) and KCDRs 1 and 3 (light teal and deep teal, respectively) contribute to 5D5 Fab recognition, whereas KCDR2 (teal) does not. (D) Electrostatic surface potential of mAb 5D5 bound to PfCSP81–92. mAb 5D5 displays extensive shape and charge complementarity to PfCSP. Electrostatic calculations were performed using Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver (APBS; Baker et al., 2001) and rendered in PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0; Schrödinger, LLC); scale: −5 kT/e (red) to +5 kT/e (blue). (E) H-bonds (shown as black dashed lines) formed between mAb 5D5 HCDR residues and negatively charged PfCSP residues. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. αTSR, α-thrombospondin type 1 repeat. GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol. kT/e, unit of electrostatic potential.