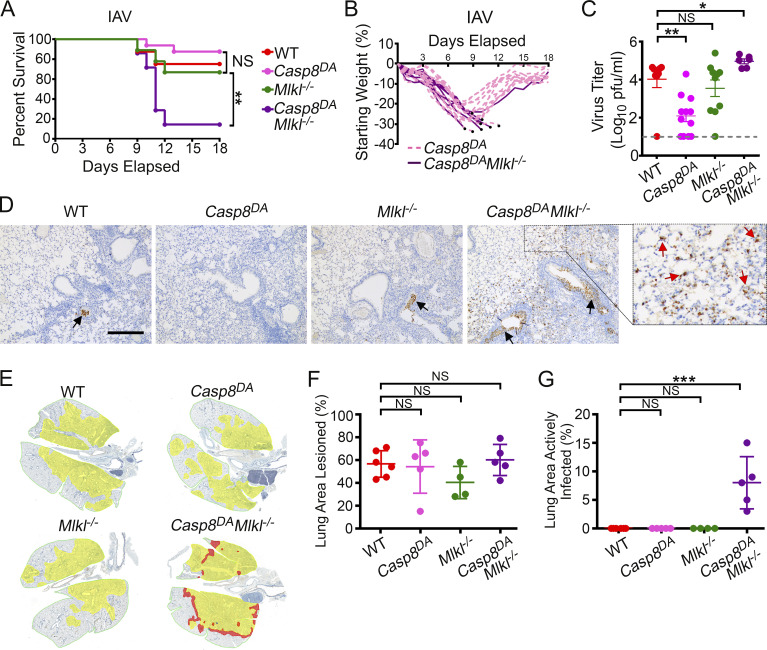
Figure 3.
Necroptosis protects against IAV in the absence of apoptosis. (A) Survival analysis of 8–12-wk-old sex-matched mice of the indicated genotypes (WT, n = 8; Casp8DA, n = 13; Mlkl−/−, n = 7; Casp8DAMlkl−/−, n = 7) following infection with PR8 (2,500 EID50/mouse). (B) Weight loss analysis of Casp8DA and Casp8DAMlkl−/− mice shown in A. Dead mice are represented by black circles. Casp8DA, n = 13; Casp8DAMlkl−/−, n = 7. (C) Lung virus titers of mice of the indicated genotypes at 9 d.p.i. with PR8 (1,500 EID50). WT, n = 8; Casp8DA, n = 12; Mlkl−/−, n = 10; Casp8DAMlkl−/−, n = 6. (D) Staining for IAV antigen in the lung at 9 d.p.i. with PR8 (1,500 EID50). Red arrows show actively infected cells in lungs of Casp8DAMlkl−/− mice. Black arrows point to antigen-positive extracellular virus debris. Scale bar = 300 µm. (E) Morphometry of virus spread. Alveolar areas containing virus antigen–positive cells are highlighted in red, and lesioned areas with no/minimal antigen-positive debris are shown in yellow. (F) Percentage of infected lungs with lesioned areas, calculated from the morphometric images shown in E. WT, n = 6; Casp8DA, n = 5; Mlkl−/−, n = 4; Casp8DAMlkl−/−, n = 5. (G) Percentage of infected lung showing areas of active infection, calculated from the morphometric images shown in E. WT, n = 6; Casp8DA, n = 5; Mlkl−/−, n = 4; Casp8DAMlkl−/−, n = 5. Data are representative of (A and B) or pooled from (C–G) two independent experiments. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (A); Mann-Whitney test (C); one-way ANOVA comparing WT samples with every other genotype (G and H). Error bars represent mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.00005.