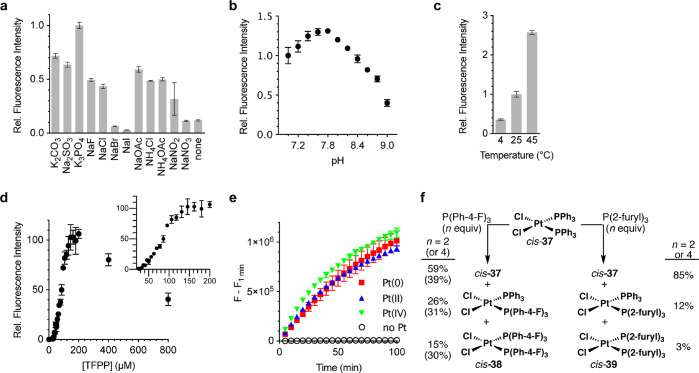
Figure 3.
Optimization of reaction conditions for selectivity and sensitivity of APE toward Pt. n = 3. (a) Relative fluorescence intensity with various salts. Conditions: 510 nM Pt, 20 μM APE, 200 μM TFPP, 1:9 (v/v) DMSO/125 mM salt, pH 7.0, 25 °C, 10 min. (b) Relative fluorescence intensity at different pH values. Conditions: 510 nM Pt, 20 μM APE, 200 μM TFPP, 1:9 (v/v) DMSO/1.2 M phosphate, pH 7.0–9.0, 25 °C, 45 min. (c) Relative fluorescence intensity at different temperatures. Conditions: 250 nM Pt, 20 μM APE, 400 μM TFPP, 1:9 (v/v) DMSO/1.2 M phosphate, pH 7.8, 30 min. (d) Correlation between the concentrations of TFPP and the deallylation rate of APE. Conditions: 510 nM Pt, 20 μM APE, 1:9 (v/v) DMSO/1.2 M phosphate, pH 7.8, 25 °C, 1 h. n = 3. (e) Preincubation of various Pt species with TFPP. Conditions: 1 μM Pt, 20 μM APE, 200 μM TFPP, 1:9 (v/v) DMSO/1.2 M phosphate, pH 7.8, 25 °C, n = 3. (f) Reactions of cis-37 with TFPP or P(2-furyl)3 in CDCl3.