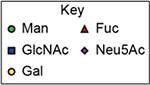
Table 1.
Summary of lectin specificities observed in this study. Shaded in grey indicates the binding epitope for each lectin. The red x shows the additional sequence in certain positions significantly reduces lectin binding. The symbol +/− means the substitution can be tolerated by the lectin. The table also shows whether α2,3-, α2,6-sialic acid and core fucose are tolerated by each lectin. The symbolic nomenclature for glycans are shown in Fig. 1.
| Lectin | Sequence | Tolerance of other modifications | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α2,3-Neu5Ac | α2,6-Neu5Ac | core Fuc | ||
| WGA | 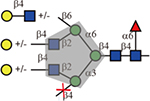 |
Yes | No | Yes |
| DSA | 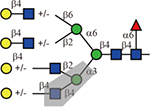 |
Yes | No | Yes |
| LCA or PSA | 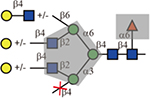 |
Yes | Yes | Must |
| L-PHA | 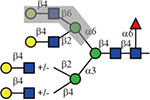 |
Yes | No | Yes |
| E-PHA | 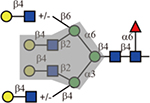 |
Yes | No | Yes |
| ConA | 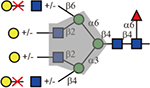 |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
| GNA | high mannose N-glycans | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| GSL-II | No | No | Yes | |
| ECL | 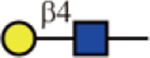 |
No | No | Yes |
| RCA-I | 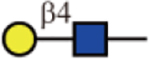 |
No | Yes | Yes |
| SNA | 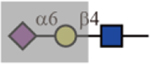 |
No | N/A | Yes |
| MAL-I | 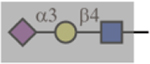 |
N/A | No | Yes |
| AAL | 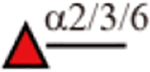 |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
| UEA-I | Not bound on this array | |||