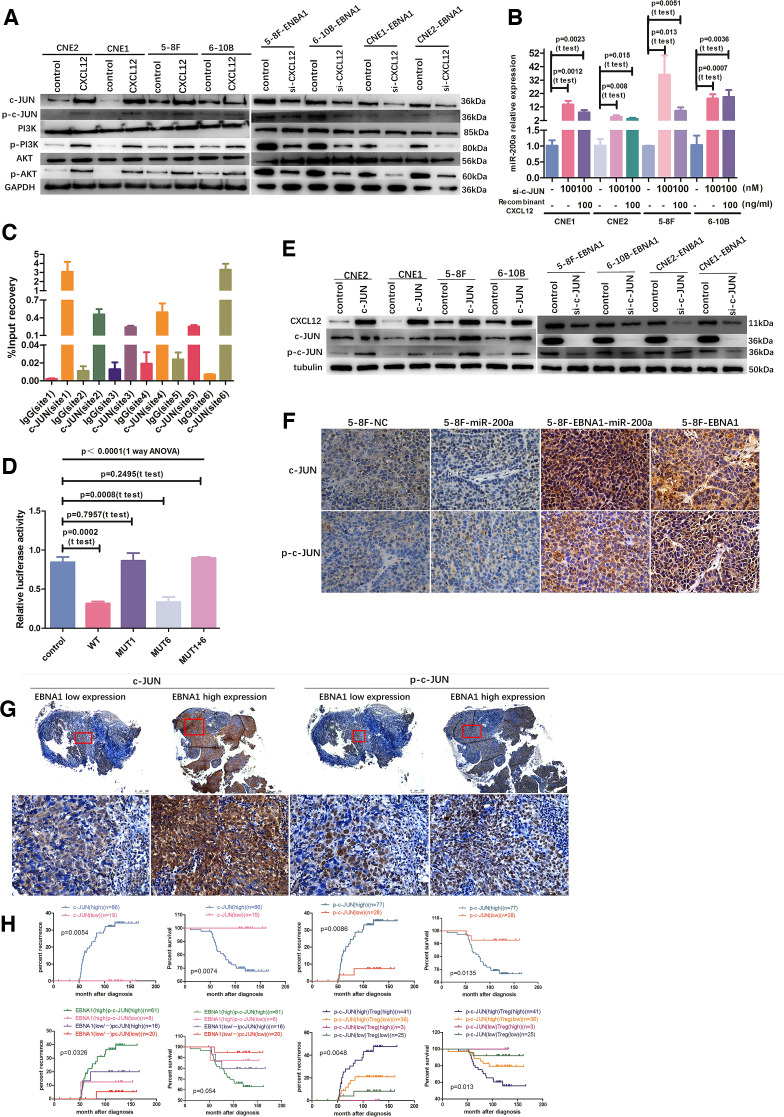
Figure 4.
c-JUN directly binds to miR-200a promoter and generates a c-JUN-miR-200a-CXCL12- PI3K-AKT-c-JUN feedback loop. (A) Overexpression of CXCL12 increased PI3K-AKT-c-JUN signaling expression; however, CXCL12-specific siRNA decreased the PI3K-AKT-c-JUN signaling pathway expression. (B) The c-JUN-specific siRNAs increased miR-200a level after blockade of c-JUN and rescued the suppressive effect of CXCL12 overexpression on miR-200a transcription. (C) ChIP assay demonstrated c-JUN binding to the miR-200a promoter region at site1 and site6. (D) miR-200a promoter dual luciferase reporter assay verified that c-JUN directly binds to miR-200a promoter. (E) c-JUN positively regulates CXCL12 expression. (F) IHC detection of c-JUN and p-c-JUN expression in various NPC xenograft groups from figure 3F1. Scale bars at the bottom right: 75 μm. (G) Representative c-JUN and p-c-JUN expression in NPC patients in EBNA1 low and high expression groups according to IHC. Scale bars at the bottom right: 500 μm (low magnification) and 75 μm (high magnification). (H) Kaplan-Meier analysis of recurrence risk and overall survival for c-JUN and phospho-c-JUN expression groups, and the recurrence risk and overall survival for the concurrent EBNA1/p-c-JUN expression groups and the concurrent p-c-JUN expression and infiltration of Treg cells groups in 105 NPC patients. ANOVA, analysis of variance; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; Treg, regulatory T.