Figure 1. The 3 subfamilies of the IL-1 family.
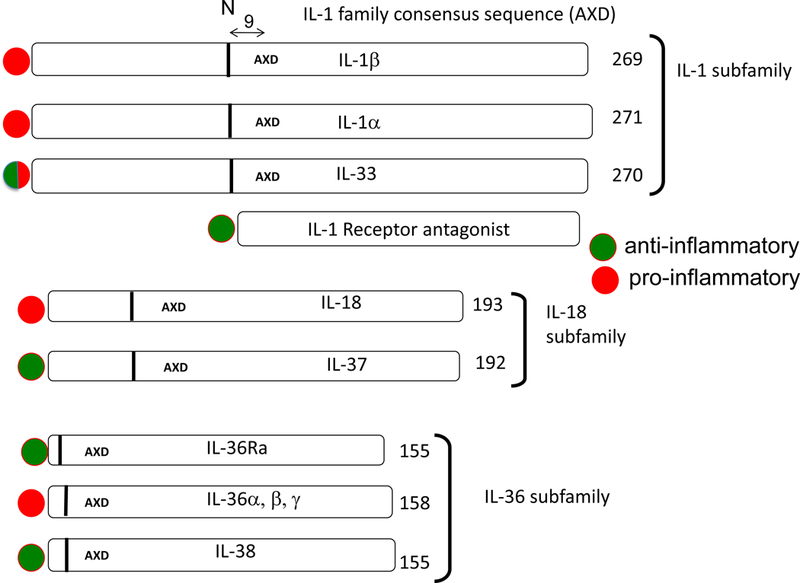
The lengths of the precursors are shown with the number of amino acids indicated at the end of each cytokine. The location of IL-1 family consensus sequence AXD is indicated in each precursor. In consensus sequence AXD, the A is an aliphatic amino acid, X is any amino acid and then D is always aspartic acid. The aspartic acid D is not the aspartic acid for the recognition of caspase-1 cleavage. Nine amino acids preceding the AXD site is a vertical bar. The vertical bar indicates the location of the optimal N-terminus. The processing enzymes of the precursors that result in an optimal N-terminus differ for each member. Some members of the IL-1 family have more than one AXD site thus creating an alternative N-terminus, for example IL-37 (137). The N-terminus affects the dimensional structure of the cytokine and therefore receptor binding and activity (138). In the case of IL-1β, nine amino acids preceding the AXD site is the caspase-1 cleavage site at amino acid 117. The IL-1 family members with proinflammatory properties are indicated by a red circle whereas a green circle represents cytokines that are anti-inflammatory. IL-1Ra is a unique member of the IL-1 family and highly homologous to IL-1β. IL-1Ra precursor has a classic signal peptide, is processed in the Golgi and readily secreted. There is an intracellular form of the IL-1Ra generated by alternate splicing. Intracellular IL-1Ra plays a role inside the cell (139). Because IL-1Ra has a signal peptide and is readily secreted, there is no AXD site.
