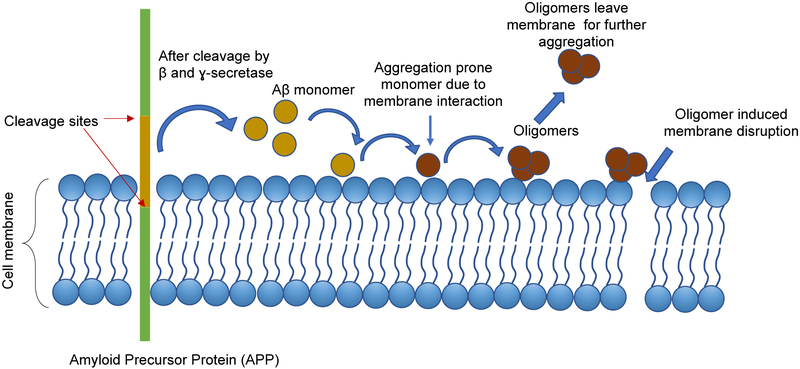
Figure 1:
Schematic showing the plausible mechanism behind the membrane induced Aβ oligomer formation followed cytotoxic effects of oligomers.
Aβ peptides are produced by proteolytic cleavage of membrane protein APP. Aβ can then self-assemble to form oligomers and fibrils, or the monomer can interact with different membrane components, including phospholipids, cholesterol or sphingolipids. These interactions can induce structural changes in Aβ and facilitate the aggregation process. The oligomers formed on the membrane can leave the surface and participate in further aggregation as seeds. Membrane-oligomer interaction could result in membrane disruption which can lead to cytotoxicity.