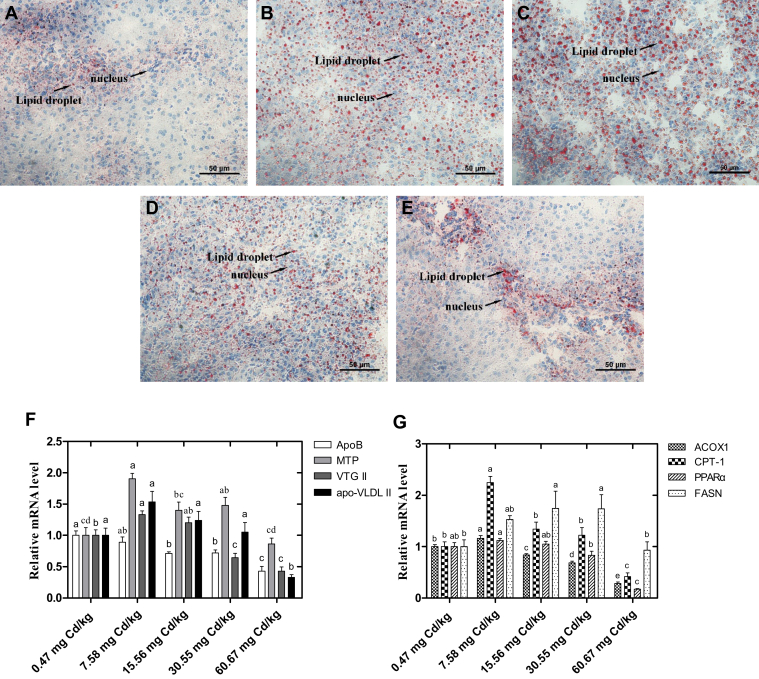
Figure 5.
Effects of Cd on the lipid deposition and metabolism in the liver of laying hens. The liver sections were stained with oil red O (400 magnification, scale bar = 50 μm). (A) Control (0.47 mg Cd/kg); (B) 7.58 mg Cd/kg; (C) 15.56 mg Cd/kg; (D) 30.55 mg Cd/kg; (E) 60.67 mg Cd/kg. (F, G) The transcript levels of genes involved in hepatic lipid metabolism. a-eColumns with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05). Method of 2−ΔΔCt was applied for calculation of relative gene expression with β-actin as the endogenous control and the average ΔCt value of 0.47 μmol Cd group as the calibrator to normalize the signal. Values were expressed as mean ± SE (n = 6). a-eColumns with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05). Abbreviations: ApoB, apolipoprotein B; MTP, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; VTG II, vitellogenin II; apo-VLDL II, apolipoprotein very-low-density lipoprotein II; ACOX1, acyl-CoAoxidase 1; CPT-1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α; FASN, fatty acid synthase.