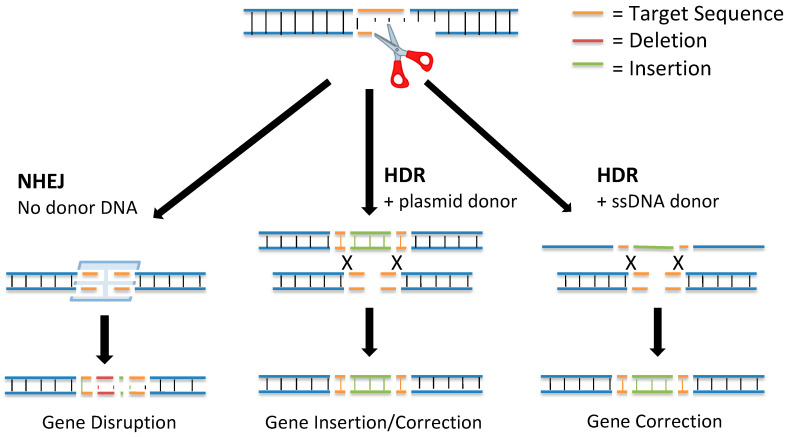
Figure 1.
DNA repair pathways. Once a nuclease has been directed to the target sequence and has bound to the DNA strands, it induces a double-strand break (DSB). The DSB is repaired by endogenous cellular repair machinery through either the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway. NHEJ-mediated repair (shown on the left) results in random indels at the break site leading to gene disruption. Alternatively, HDR-mediated repair uses a donor template DNA, either a long double-stranded plasmid (center) or an ssDNA (right), and results in the incorporation of a desired genetic sequence for the correction or insertion of a gene. This figure has been adapted from [6].