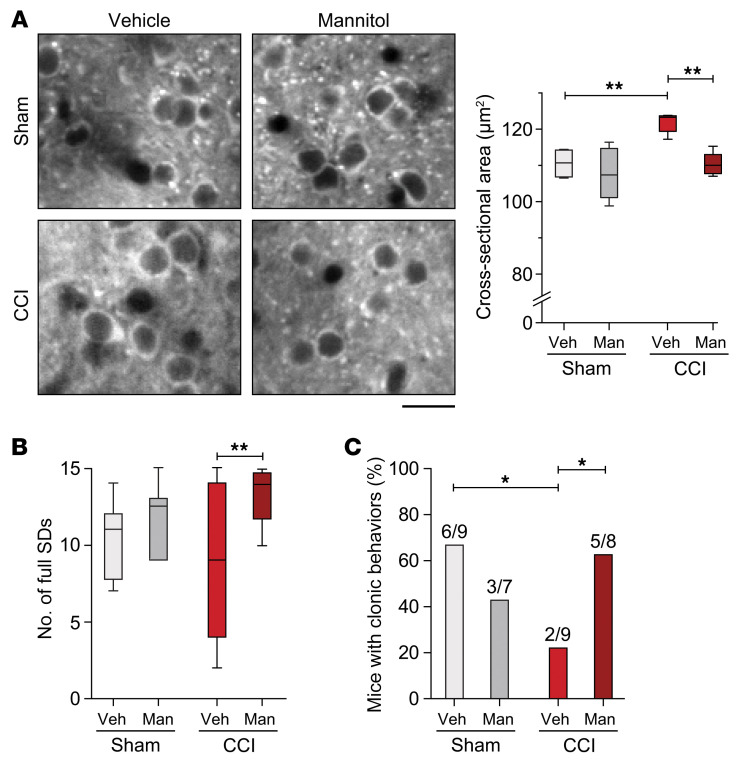
Figure 8. The osmotic diuretic mannitol reduces neuronal swelling and increases network activity.
(A) Images of representative neurons in layer 2/3 cortex during treatments. Scale bar: 25 μm. Plot of neuronal cross-sectional area shows that mannitol (Man) (3 g/kg; i.v.) reversed neuronal swelling in CCI-treated mice (P = 0.001, 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisons test; CCI-mannitol vs. vehicle: **P < 0.01; CCI-vehicle vs. sham-vehicle: **P < 0.01; n = 32–70 neurons, n = 4–5 mice per group). (B) Quantification of SD frequency based on 2-hour recordings in 1 M KCl solution showed a significant increase in SD susceptibility in CCI-mannitol– versus CCI-vehicle–treated animals (P = 0.03, Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple-comparisons test; CCI-mannitol vs. vehicle: **P < 0.01; n = 6–10 mice per group). (C) Analysis of network excitability showed a significant increase in the percentage of animals with seizures in the CCI-mannitol–treated group relative to the CCI-vehicle–treated group (CCI-mannitol vs. vehicle: *P = 0.04; CCI-vehicle vs. sham-vehicle: *P = 0.02; χ2 test; n = 7–9 mice per group; the number of mice with seizures and group size are indicated for each group.).