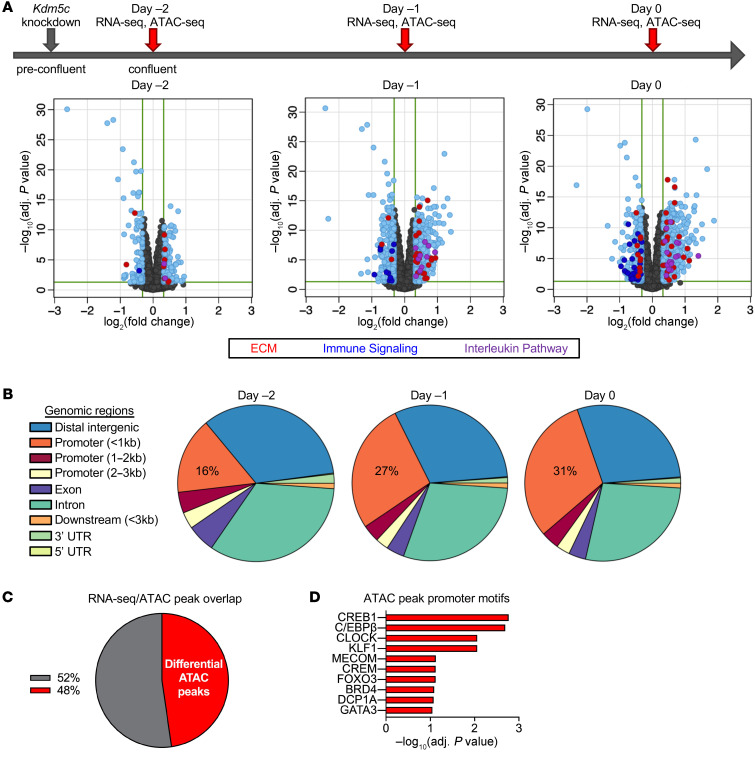
Figure 5. Kdm5c knockdown in preadipocytes alters gene expression and chromatin accessibility at promoters enriched in adipogenic transcription factor motifs.
(A) Differential gene expression induced by Kdm5c knockdown in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Top: timeline of sample generation (n = 5 samples for each treatment at each time point). Volcano plots show genes that are differentially expressed (EdgeR) in response to Kdm5c knockdown (light blue dots). Differentially expressed genes with greater than 1.25-fold difference were analyzed for pathway enrichment, and genes belonging to 3 most significant pathways are highlighted with colored dots: red dots, genes involved in ECM organization (ECM); dark blue dots, genes in immune signaling pathways; purple dots, genes in interleukin pathway. (B) ATAC-Seq analysis of the same samples in A showed altered chromatin accessibility after Kdm5c knockdown at genomic locations indicated (n = 4 samples for each treatment at each time point). Alterations at proximal gene promoters (within 1.5 kb of transcription start sites) progressively increased each day after knockdown. (C) Differentially expressed genes from day 0 were overlaid with differential ATAC-Seq promoter peaks from day 0, and 48% of the corresponding genes showed overlap in the 2 data sets. (D) Genes that showed differential mRNA expression and ATAC-Seq promoter peaks showed enrichment for specific transcription factor motifs in the promoter region.