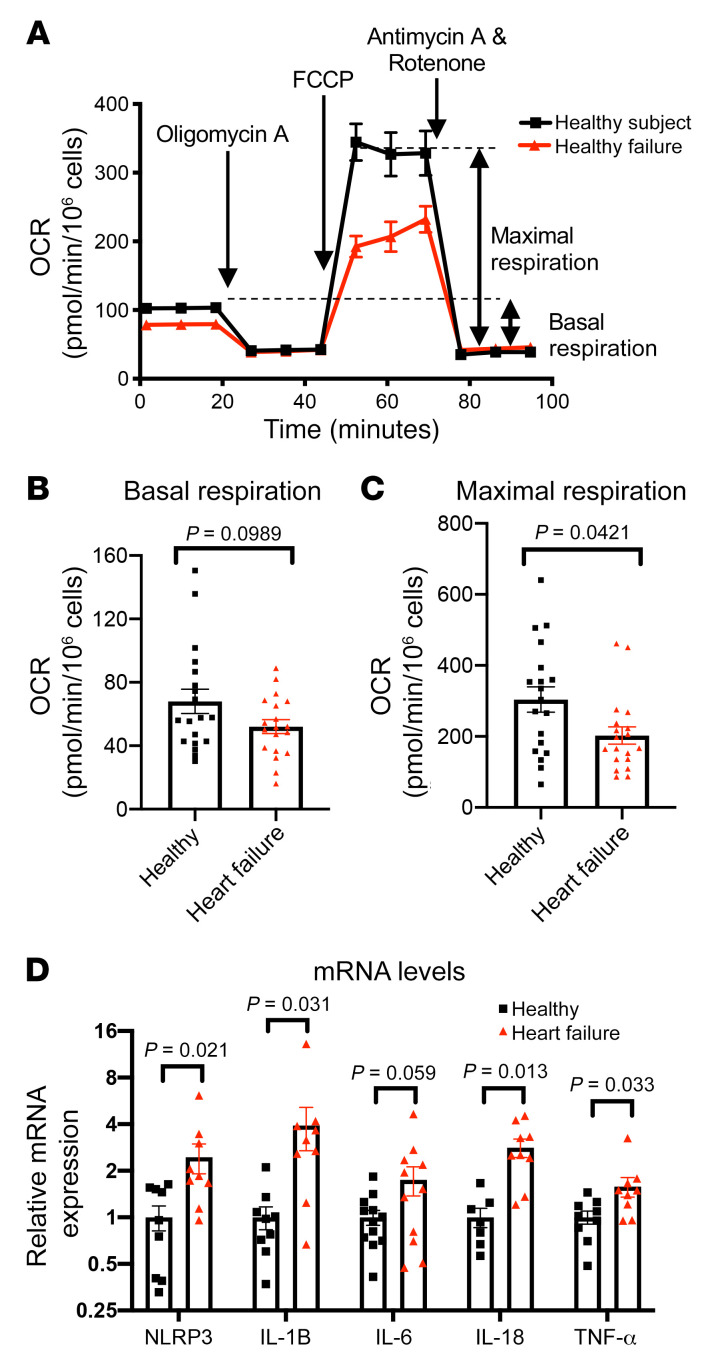
Figure 1. Heart failure is associated with a reduced maximal respiration and elevated proinflammatory cytokine gene expressions in PBMCs.
(A) Representative OCR plot upon various inhibitor injections in a standard Seahorse Mito stress test, comparing PBMCs from healthy subjects and those with stage D HF. Oligomycin A: inhibitor of complex V. FCCP (trifluoromethoxy carbonylcyanide phenylhydrazone): uncoupling agent by permeabilizing inner mitochondrial membrane. Antimycin A: inhibitor of complex III. Rotenone: inhibitor of complex I. (B and C) Basal and FCCP-induced maximal respiration of PBMCs from healthy subjects (n = 19) and subjects with stage D HF (n = 19), respectively. OCR data normalized via log10 transformation were subjected to ordinary unpaired 2-tailed parametric test (Welch’s t test). Normal distribution was assessed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. (D) Relative mRNA levels of NLRP3 and proinflammatory cytokines of PBMCs of healthy subjects and those with stage D HF by RT-qPCR. NLRP3 (healthy n = 9, HF n = 9), IL-1B (n = 9, n = 9), IL-6 (n = 12, n = 11), IL-18 (n = 7, n = 9), TNF-α (n = 9, n = 9). Mean mRNA level of healthy subjects normalized to 1. mRNA data analyzed with unpaired nonparametric 2-tailed t test. All data shown in mean ± SEM.