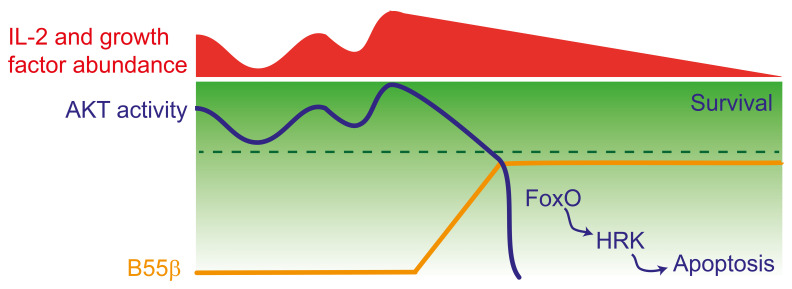
Figure 9. Decreased AKT activity induces B55β transcription, which halts further AKT activation.
AKT activity fluctuates in response to nutrient and growth factor abundance. When AKT activity decreases under a certain threshold (indicated by the broken line), for example, during IL-2 withdrawal or AKT silencing, expression of B55β is induced. By promoting AKT dephosphorylation, B55β actively inhibits further AKT activity and commits the cell to apoptosis through the activation of FoxO and the induction of HRK.