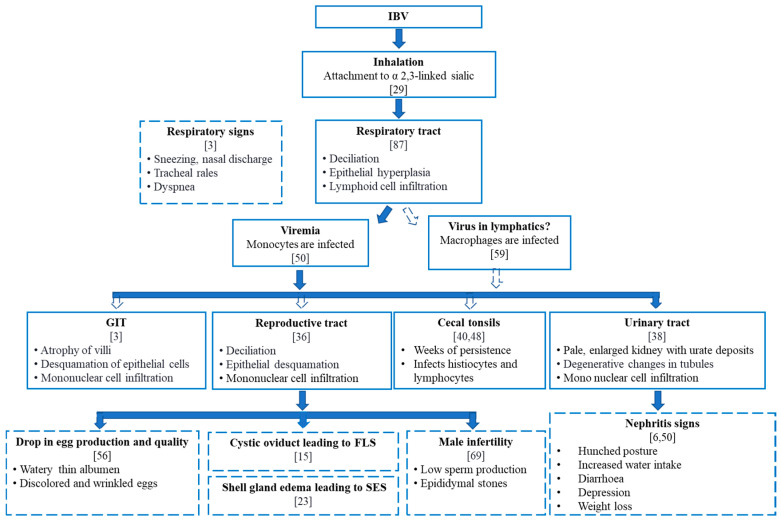
Figure 2.
Clinical and pathological manifestations of IBV infection. The schematic diagram shows the entry, the route of dissemination of the virus to visceral organs and the pathogenesis of various IBV strains in different body systems. All the IBV strains primarily infect the respiratory tract, and based on the genotypes, the IBV infection can extend to various tissues, either persisting or leading to clinical and pathological manifestations. The solid arrows indicate paths that have been confirmed. The empty arrows indicate paths that have been suggested. The text boxes with continuous borders summarize histological changes, and the text boxes with discontinuous borders represent clinical manifestations. SES, shell-less egg syndrome; FLS, false layer syndrome; GIT, gastrointestinal tract.