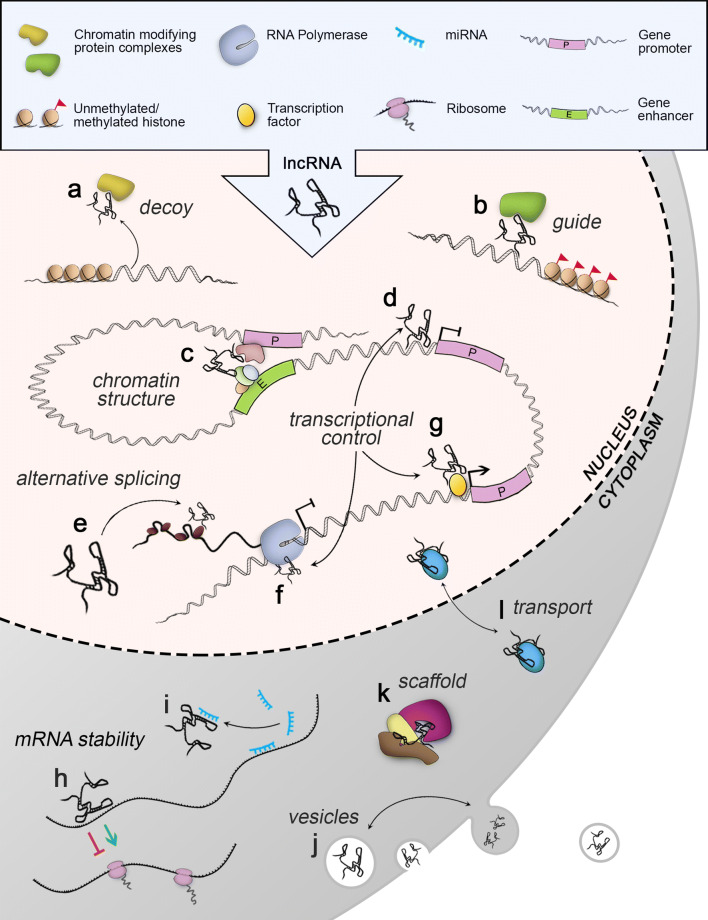
Fig. 1.
Molecular functions of lncRNAs. Nuclear lncRNAs can regulate epigenetic changes by a decoying or b guiding chromatin-modifying complexes to specific genomic loci. c lncRNAs can induce chromosomal looping to control gene expression by simultaneously binding to protein complexes or specific DNA elements. LncRNAs can inhibit gene transcription d by blocking a transcription factor binding site or f by binding to RNA polymerase. g LncRNAs may contribute to transcriptional activation by guiding transcription factors or other co-factors to gene promoters. e LncRNAs can regulate alternative splicing that can occur by lncRNA binding to mRNA and blocking the splice-site. LncRNAs can also recruit and guide splicing factors to the sites of transcription. Cytoplasmic lncRNAs can regulate mRNA stability h directly by binding to mRNAs or i indirectly by sequestering miRNAs by complementary base pairing. j Some lncRNAs can be secreted to extracellular vesicles or exosomes allowing them to mediate intercellular signaling. k LncRNAs can serve as scaffolds to promote the assembly of active ribonucleoprotein complexes in the cytoplasm or nucleus. l LncRNAs can aid intracellular translocation of proteins