Fig. 5.
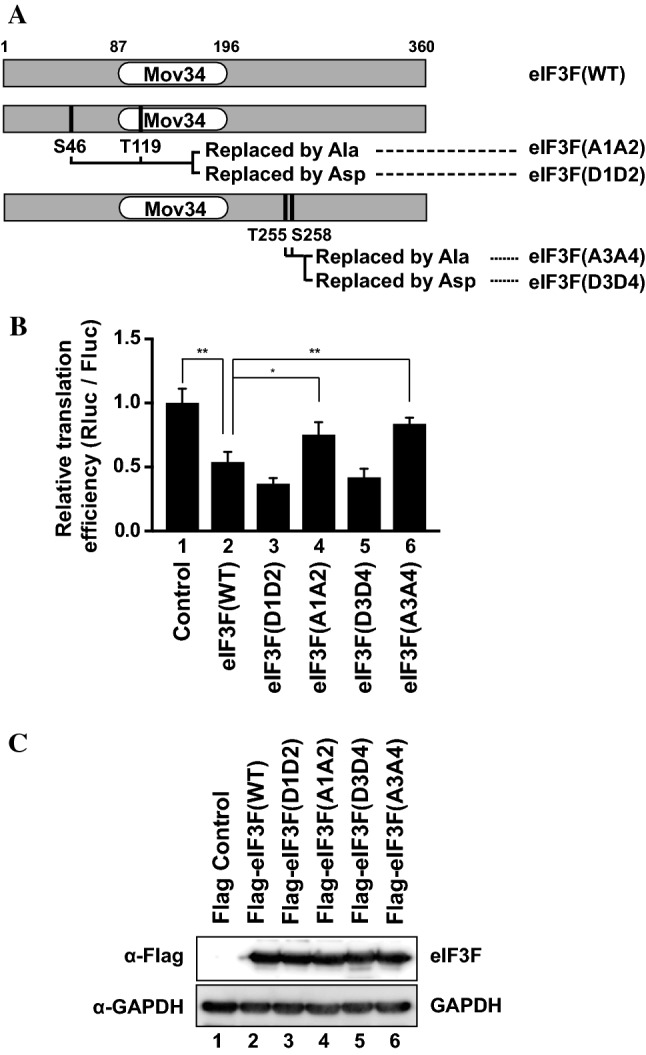
Unphosphorylatable mutants of eIF3F do not repress translation. a Schematic diagrams of phospho-mimetic mutants [eIF3F(D1D2) and eIF3F(D3D4)], and unphosphorylatable mutants [eIF3F(A1A2) and eIF3F(A3A4)] of eIF3F. b The effects of ectopic expression of eIF3F(WT) and its derivatives on cap-dependent translation were monitored as described in Fig. 1 except that effector plasmids encoding eIF3F derivatives instead of CDK11 isoforms were used. The relative cap-dependent translation efficiencies, which were normalized to CrPV IRES-dependent translation activity in each sample, are depicted. The cap-dependent translation activity in control vector-transfected cells was set to 1 (lane 1). Experiments were repeated three times with duplicate samples. The columns and bars represent the means and ± standard deviations, respectively. Asterisk (*) depicts P < 0.05, lane 4 compared with lane 2. Asterisks (**) depict P < 0.005, lane 6 compared with lane 2. c The levels of ectopically expressed proteins (eIF3F and its derivatives) in cells were monitored by western blotting using an anti-Flag antibody. The level of GAPDH protein was also monitored using an anti-GAPDH antibody as an endogenous protein control
