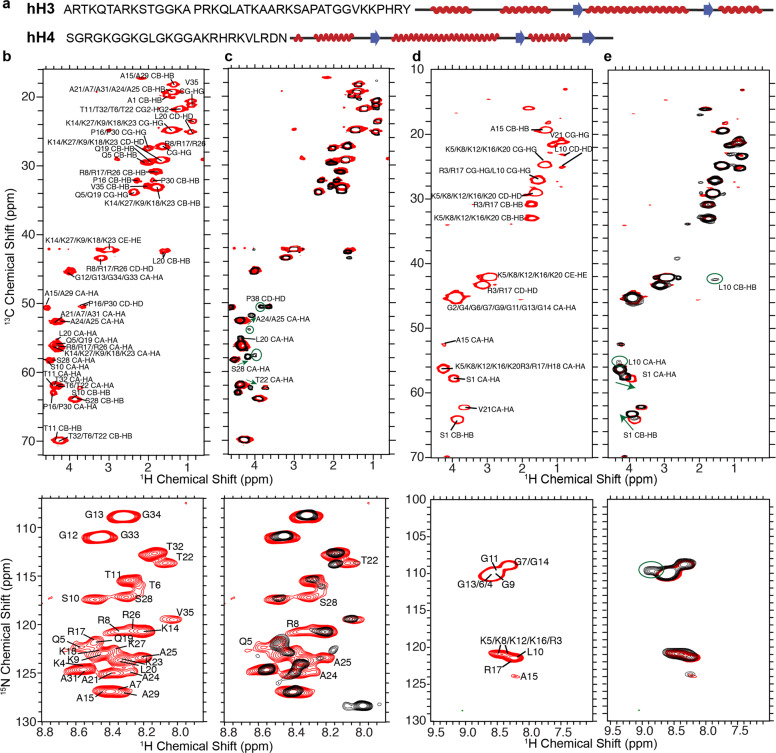
Fig. 7. hH3 and hH4 tails are more dynamic in the telomeric NCP in comparison with the Widom 601 NCP.
a Schematic representations of hH3 and hH4 tail sequences and secondary structures. b 1H–13C (upper panel) and 1H–15N (lower panel) correlation SSNMR spectra of the Widom 601 NCP containing uniformly 13C,15N-labeled hH3. c The overlaid 1H–13C (upper panel) and 1H–15N (lower panel) correlation SSNMR spectra of the Widom 601 NCP (red) and telomeric NCP (black) containing uniformly 13C,15N-labeled hH3. d The 1H–13C (upper panel) and 1H–15N (lower panel) correlation SSNMR spectra of the Widom 601 NCP containing uniformly 13C,15N-labeled hH4. e The overlaid 1H–13C (upper panel) and 1H–15N (lower panel) correlation SSNMR spectra of the Widom 601 NCP (red) and telomeric NCP (black) containing uniformly 13C,15N-labeled hH4. These spectra were obtained with 2D refocused J-based INEPT pulse schemes. In c, e, arrows point the peaks shifting between the Widom 601 NCP and the telomeric NCP, circles highlight peaks observed in the telomeric NCP, but not in the Widom 601 NCP.