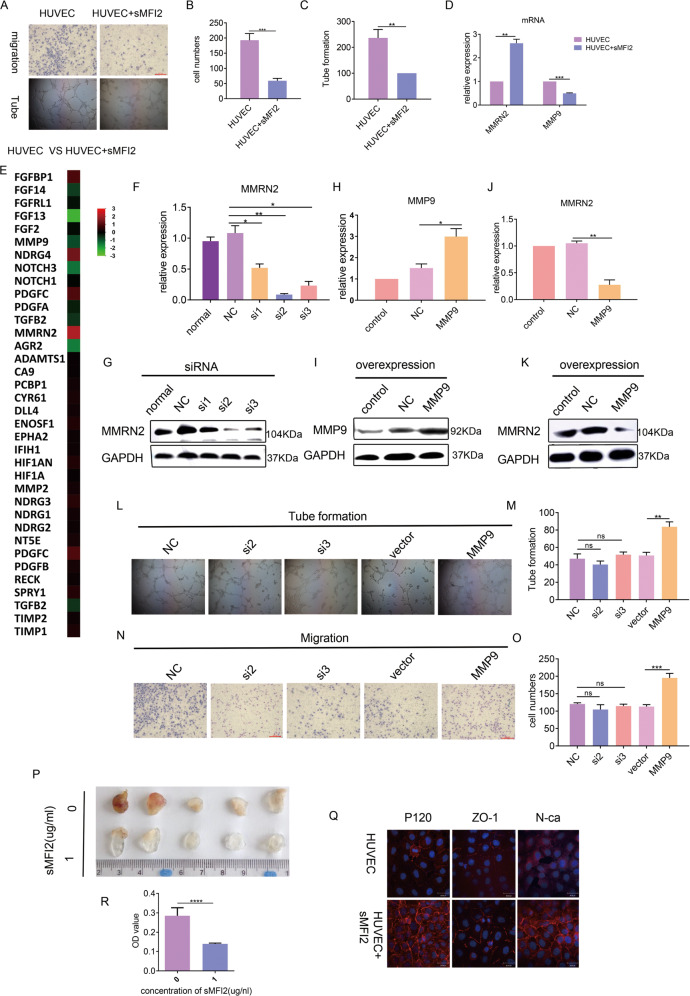
Fig. 5. sMFI2 inhibits vascular endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis via a paracrine pathway without affecting vascular permeability.
A–C Changes in migration ability and angiogenic ability of vascular endothelial cell HUVEC after co-culturing with recombinant sMFI2. D RT-PCR analysis of the expression changes of MMRN2 and MMP9 genes in HUVECs with sMFI2 co-culture or non-co-culture. E Heat map showed differential expression of common angiogenesis-related genes in HUVEC with sMFI2 co-cultured or non-co-cultured groups. The screening criterion was fold change ≥2, p < 0.05. F, G RT-PCR and western blot showed the knockdown efficiency of MMRN2 after transient transfection of siRNA. H, I RT-PCR and western blot showed overexpression efficiency of MMP9 after transient transfection of overexpressing plasmid. J, K RT-PCR and western blot showed changes in the expression of MMRN2 after overexpression of MMP9. L–O Changes in migration ability of vascular endothelial cells and tubule formation ability after knockdown of MMRN2 or overexpression of MMP9. Image taken under a ×100 microscope. Histogram showed the number of HUVEC cells and the quantification of vascularization between groups. P–R Representative pictures of angiogenesis in HUVEC under co-culture or non-co-culture conditions with recombinant sMFI2. Bar graph showed the relative content of hemoglobin between two groups. Q Immunofluorescence showed changes in intercellular junction markers P120, ZO-1, and N-cadherin of HUVEC under co-culture and non-co-culture conditions with sMFI2. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.