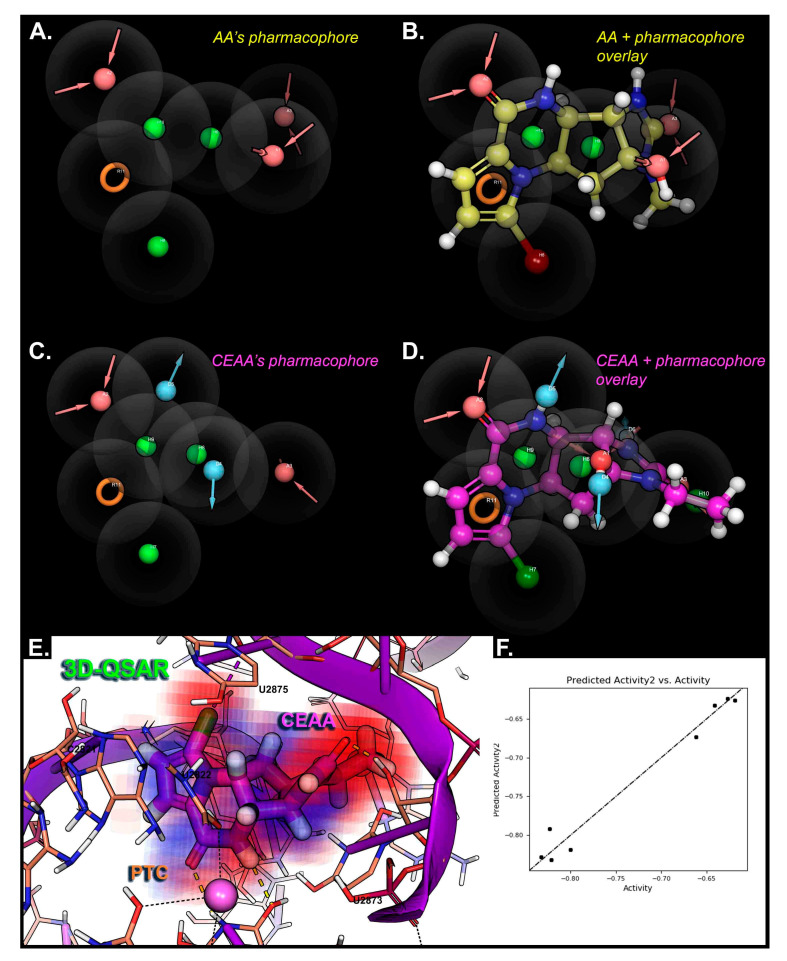
Figure 6.
Three-dimensional-quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) modeling for AA analogues binding within the PTC of the ribosome. (A) AA pharmacophore hypothesis is generated for the most useful features that can selectively bind and be used for 3D-QSAR modeling. (B) Overlay of the AA compound structure with the pharmacophore features for AA that have some interactional basis with PTC. (C) CEAA pharmacophore hypothesis is given for features most commonly occurring in PTC binding during modeling and dynamics studies. (D) Overlay of the CEAA compound structure with the pharmacophore features having an interactional basis with PTC. (E) 3D-QSAR map for CEAA within the PTC as bound. Here, the factors from a PLS-2 quantify the distribution of contributions: electrostatics (electron-withdrawing), hydrophobic/non-polar, and H-bond donors. The combined effects are “voxelized” into 0.5-Å3 units with red-to-blue color scheme giving the essential interaction sites on CEAA with the PTC (ribosome). (F) Graph for correlation between the prediction and actual activities of the 8 AA analogs is given, where R2 > 0.97, SD 0.019, RMSE 0.01, and Pearson 0.987. This demonstrates the accuracy of our compound affinity prediction in this particular system.