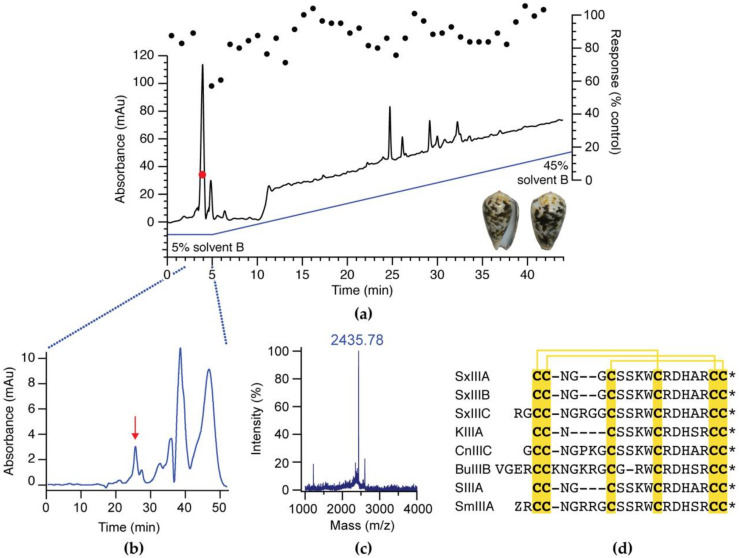
Figure 1.
Activity-guided isolation of SxIIIC from C. striolatus venom. (a) Crude venom (200 µg) isolated from one specimen of C. striolatus (inset) was fractionated and assayed for NaV inhibitor activity by fluorescence imaging in SH-SY5Y cells expressing subtypes NaV1.2, 1.3, and 1.7 (right y-axis; the activity of each fraction represented by circles overlaying the chromatogram). The bioactive component (red circle) eluted early. (b) Size-exclusion chromatography was used to further purify fractions collected between 2 and 5 min to isolate the bioactive component. The active fraction (red arrow) was dominated by (c) a mass of 2435.78 Da (m/z) and subjected to sequencing by Edman degradation, which identified a novel µ-conotoxin with a C-terminal amidation named SxIIIC. (d) Sequence alignment of SxIIIC with previously reported µ-conotoxins. * denotes C-terminal amidation.